Chiari malformation is a condition where mind tissue stretches out into your spinal canal. It happens when some portion of your skull is strangely little or deformed, pushing on your cerebrum and driving it descending.
Chiari abnormality is exceptional, yet expanded utilization of imaging tests has prompted more successive determinations.
Specialists classify Chiari distortion into three sorts, contingent upon the life systems of the cerebrum tissue that is uprooted into the spinal canal and whether developmental variations from the norm of the brain or spine are available.
Chiari malformation type I develops as the skull and cerebrum are developing. Accordingly, signs and side effects may not happen until late youth or adulthood. The pediatric structures, Chiari abnormality type II and type III, are available during childbirth (intrinsic).
What are the risk factors?
There's some proof that Chiari abnormality runs in certain families. Be that as it may, the investigation into a potential innate segment is still in its beginning stage.
Types of Chiari malformation
Numerous individuals with Chiari malformation have no signs or manifestations and needn't bother with treatment. Their condition is distinguished just when tests are performed for irrelevant issues. Notwithstanding, contingent upon the sort and seriousness, Chiari mutation can cause various issues.
The more normal sorts of Chiari abnormality are:
- Type I
- Type II
In spite of the fact that these sorts are less genuine than the more uncommon pediatric structure, type III, signs side effects despite everything that can be life-disrupting.
- Chiari malformation type I
In Chiari malformation type I, signs and indications normally show up during late adolescence or adulthood.
Migraines, regularly extreme, are the exemplary indication of Chiari malformation. They by and large happen after unexpected coughing, sneezing, or stressing. Individuals with Chiari malformation type I can likewise understanding:
- Neck torment
- Unsteady step (issues with balance)
- Poor hand coordination (fine engine abilities)
- Numbness and shivering of the hands and feet
- Dizziness
- Difficulty gulping, some of the time joined by choking, stifling, and retching
- Speech issues, for example, hoarseness
Less frequently, individuals with Chiari abnormality may experience:
- Ringing or humming in the ears (tinnitus)
- Weakness
- Slow heart musicality
- The curvature of the spine (scoliosis) identified with spinal string debilitation
- Abnormal breathing, for example, focal rest apnea, which is the point at which an individual quits breathing during rest
2. Chiari malformation type II
In Chiari malformation type II, a more prominent measure of tissue reaches out into the spinal canal contrasted and Chiari malformation type I.
The signs and side effects can incorporate those identified with a type of spina bifida considered myelomeningocele that consistently goes with Chiari malformation type II. In myelomeningocele, the spine and the spinal trench haven't shut appropriately before birth.
3. Chiari malformation type III
In one of the most serious sorts of the condition, Chiari malformation type III, a bit of the lower back aspect of the cerebrum (cerebellum) or the brainstem stretches out through an unusual opening in the back of the skull. This type of Chiari malformation is determined during childbirth or to have an ultrasound during pregnancy.
This sort of Chiari malformation has a higher death rate and may likewise cause neurological issues.
Causes of Chiari malformation
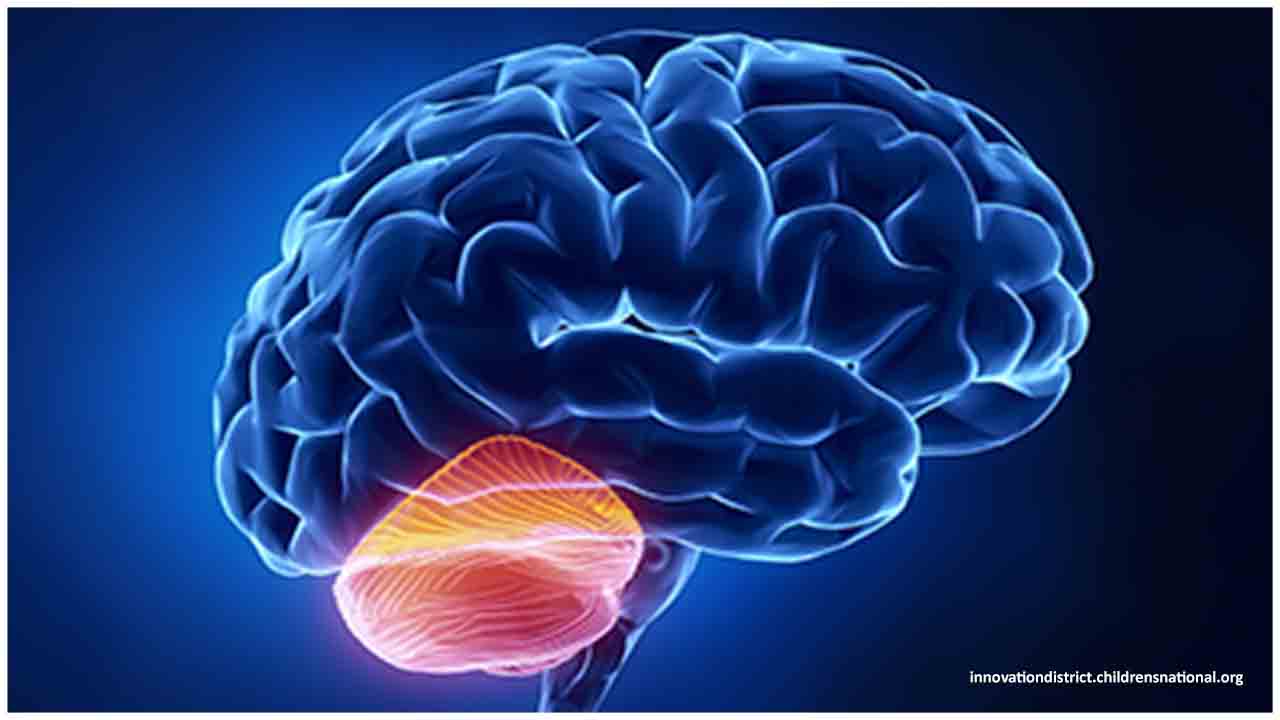
Chiari malformation type I happens when the area of your skull containing an aspect of your mind (cerebellum) is excessively little or is distorted, along these lines squeezing and swarming your cerebrum. The lower part of the cerebellum (tonsils) is dislodged into your upper spinal cord.
Chiari mutation type II is almost consistently connected with a type of spina bifida called myelomeningocele.
At the point when the cerebellum is driven into your upper spinal canal, it can meddle with the ordinary progression of cerebrospinal liquid that secures your cerebrum and spinal cord. This hindered flow of cerebrospinal liquid can prompt the blockage of signs communicated from your cerebrum to your body, or to the development of spinal liquid in the mind or spinal cord. On the other hand, the weight from the cerebellum on the spinal string or lower brainstem can cause neurological signs or side effects.
Signs and manifestations may include:
- Changes in breathing example
- Swallowing issues, for example, choking
- Quick descending eye developments
- Weakness in arms
Chiari contortion type II is normally noted with ultrasound during pregnancy. It might likewise be analyzed after birth or in the early earliest stages.
What are the complexities?
In certain individuals, Chiari malformation can turn into a dynamic issue and lead to genuine complexities. In others, there might be no related side effects, and no mediation is fundamental. The difficulties related to this condition include:
- Hydrocephalus
A gathering of abundance liquid inside your cerebrum (hydrocephalus) may require situation of an adaptable cylinder (shunt) to occupy and deplete the cerebrospinal liquid to another territory of your body.
- Spina bifida
Spina bifida, a condition wherein your spinal string or its covering isn't completely evolved, may happen in Chiari malformation. Some portion of the spinal cord is uncovered, which can cause genuine conditions, for example, loss of motion. Individuals with Chiari malformation type II typically have a type of spina bifida called myelomeningocele.
- Syringomyelia
A few people with Chiari malformation additionally build up a condition called syringomyelia, in which a cavity or pimple (syrinx) structures inside the spinal cord.
- Tethered line disorder
In this condition, your spinal cord appends to your spine and makes your spinal cord stretch. This can cause genuine nerve and muscle harm in your lower body.
Treatment
Treatment of Chiari malformation relies upon the structure, seriousness, and related side effects. Normal observing, drugs, and medical procedure are therapy choices. At times, no treatment is required.
When to see a specialist
On the off chance that you or your kid has any of the signs and manifestations that might be related to Chiari malformation, see your PCP for an assessment.
Since numerous manifestations of Chiari malformation can likewise be related to different issues, a careful clinical assessment is significant.
 Chiari mutation type II is almost consistently connected with a type of spina bifida called myelomeningocele.
Chiari mutation type II is almost consistently connected with a type of spina bifida called myelomeningocele.









.jpeg)






.jpg)




.jpg)





.jpeg)
