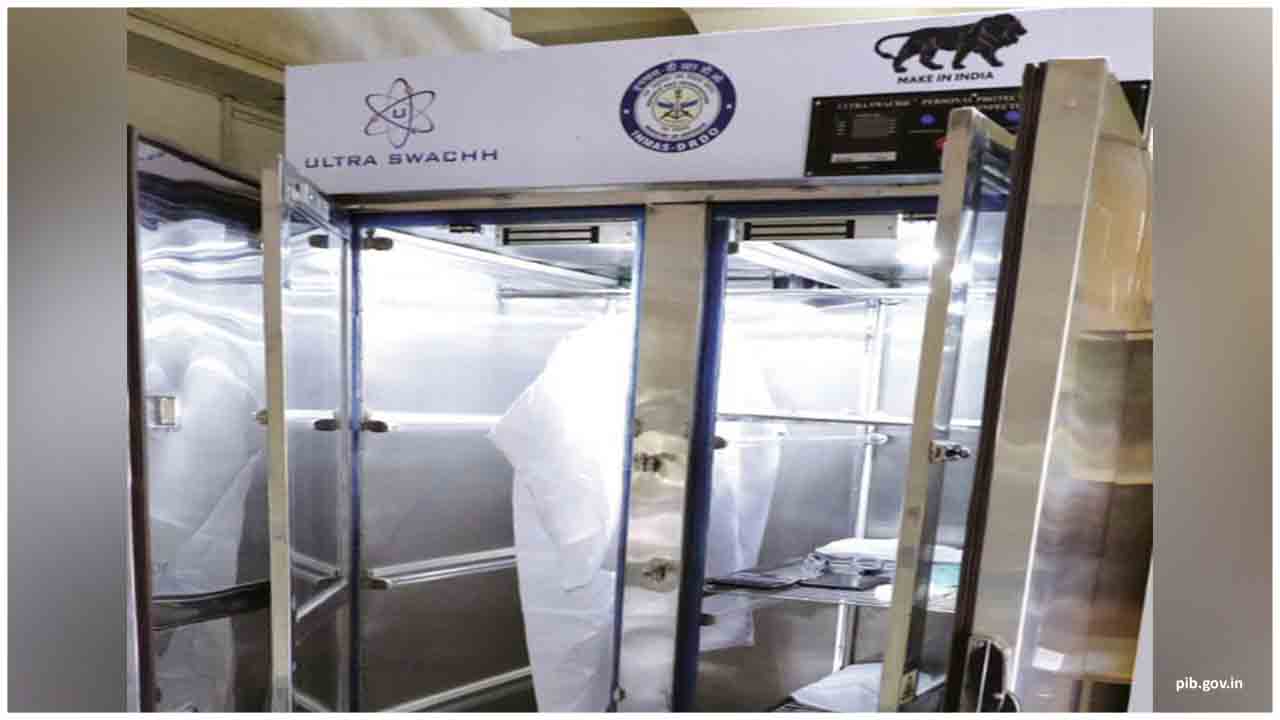
Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) has developed a disinfection unit named Ultra Swachh to disinfect a wide range of materials, including Personal Protective Equipment (PPEs), electronics items, fabrics and others.
Institute of Nuclear Medicine and Allied Sciences, the Delhi-based laboratory of DRDO has developed this product with industry partner Gel Craft Health care Private Ltd. The system uses an advanced oxidative process comprising of multiple barrier disruption approach using Ozonated Space Technology for disinfection.
Ultra Swachh is double-layered, with specialized Ozone sealant technology assuring trapping of Ozone for the necessary disinfection cycle. It also has catalytic converter to ensure environment friendly exhaust. The system is in compliance with International Standards of Industrial, Occupational, Personal and Environmental Safety.
Ultra Swachh comes in two variants namely Ozonated Space and Trinetra Technology. Trinetra technology is the combination of Ozonated space and radical dispenser. Treatment is optimized with automation for quick disinfection cycle.
Riding on innovations the premier research organization recently released an innovation from a critical technology that would help the pilots of the Indian Air Force (IAF) flying the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas with a non-stop supply of oxygen while undertaking long-endurance missions is now being offered to hospitals combating the coronavirus.
This product by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), is in the form of a Medical Oxygen Plant (MOP), is a byproduct of technology from the Onboard Oxygen (OBOX) generation system being developed for the Tejas.
The MOP technology is developed by Defence Bioengineering and Electromedical Laboratory (DEBEL), a life sciences wing of DRDO s in Bengaluru’s C.V. Raman Nagar.
MOP utilizes pressure swing adsorption (PSA) technique and molecular sieve technology to generate oxygen directly from atmospheric air
The OBOX technology for Tejas being developed by DEBEL has been approved by the Centre for Military Airworthiness and Certification (CEMILAC), an agency mandated to certify the products being transferred to a Coimbatore-based firm.
Recentky,Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Research Centre Imarat (RCI), has developed an automated contactless UVC sanitisation cabinet, calledDefence Research Ultraviolet Sanitiser (DRUVS). It has been designed to sanitise mobile phones, iPads, laptops, currency notes, cheque leafs, challans, passbooks, paper, envelopes, etc.
The DRUVS cabinet is having contactless operation which is very important to contain the spread of virus. The proximity sensor switches, clubbed with drawer opening and closing mechanism, makes its operation automatic and contactless. It provides 360 degree exposure of UVC to the objects placed inside the cabinet. Once the sanitisation is done, the system goes in sleep mode hence the operator need not wait or stand near the device.
The RCI has also developed an automated UVC currency sanitising device, called NOTESCLEAN. Bundles of currency notes can be sanitised using DRUVS, however disinfection of each currency notes using it will be a time consuming process. For that purpose, a sanitising technique has been developed, where one has to just place the loose currency notes at the input slot of the device. It picks the notes one by one and makes them pass through a series of UVC lamps for complete disinfection.
Another notable initiative by the premier research organization for curbing COVID-19 pandemic, Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has developed a full-body disinfection chamber called as Personnel Sanitization Enclosure and face protection mask. The face protection mask is now supplied to hospitals in bulk.
Vehicle Research and Development Establishment in Ahmednagar, a DRDO Laboratory, has designed full-body disinfection chamber called as personnel sanitization enclosure.
“This walkthrough enclosure is designed for personnel decontamination, one person at a time. This is a portable system equipped with sanitizer and soap dispenser,” the DRDO stated.
The decontamination is started using a foot pedal at the entry. On entering the chamber, an electrically operated pump creates a disinfectant mist of hypo sodium chloride for disinfecting.
The mist spray is calibrated for operation of 25 seconds and stops automatically indicating completion of operation.
As per procedure, personnel undergoing disinfection will need to keep their eyes closed while inside the chamber.
The system consists of roof-mounted and bottom tanks with a total of 700 liters capacity. Approximately 650 personnel can pass through the chamber for disinfection until the refill is required.
“The system has see-through glass panels on sidewalls for monitoring purpose and is fitted with lights for illumination during night time operations. A separate operator cabin is provided to monitor overall operations,” it stated.
“The system has been manufactured with the help of Dass Hitachi Ltd, Ghaziabad, within a time span of four days. This system can be used for disinfection of personnel at the areas of controlled ingress and egress such as entry and exit to hospitals, malls, office buildings and critical installations,” DRDO stated.
Further, Hyderabad’s Research Centre Imarat and Chandigarh’s Terminal Ballistics Research Laboratory (TBRL) have developed face protection mask for health care professionals handling COVID-19 patients.
Its lightweight construction makes it convenient for comfortable wear for long duration. This design uses commonly available A4 size Over-Head Projection (OHP) film for face protection.
“The holding frame is manufactured using Fused Deposition Modelling (3D printing). Polylactic Acid filament is used for 3D printing of the frame,” DRDO stated.
The thermoplastic is derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane and is biodegradable. The face mask will be mass-produced using injection moulding technique for volume production.
A total 100 face shields are being produced daily in TBRL and provided to PGIMER, Chandigarh.
Similarly, 100 are produced at RCI and has been handed over to ESIC, Hyderabad.
A demand of 10,000 numbers has been received from PGIMER and ESIC Hospitals based on successful user trials.

 DRDO is leading the fight against coronavirus with their innovation led research
DRDO is leading the fight against coronavirus with their innovation led research
















.jpeg)










.jpg)
.jpeg)






.jpg)
