The landscape of healthcare education is undergoing a transformative journey, and at its forefront is the integration of simulation models. As we dive into the future, the paradigm shift towards immersive, hands-on learning experiences is reshaping how healthcare professionals are trained. Let’s explore the evolution of healthcare education through simulation models, shedding light on the innovative approaches, benefits, and promising trajectory that lies ahead.
The Rise of Simulation in Healthcare Education Traditionally, medical education heavily relied on lectures, textbooks, and clinical rotations for skill acquisition. However, the limitations of this approach, including the variability in patient encounters and ethical concerns, paved the way for simulation-based learning. Simulation models replicate real-life scenarios, allowing learners to engage in realistic, risk-free environments that mimic clinical settings.
Key Components of Simulation Models:
1. High-Fidelity Mannequins: These advanced human simulators closely mimic human physiology, providing learners with an opportunity to practice various medical procedures, from basic examinations to complex surgeries.
2. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): Immersive technologies like VR and AR create realistic, interactive environments. Learners can explore anatomy, practice surgical techniques, and simulate patient interactions through these cutting-edge tools.
3. Computer-Based Simulations: Software applications offer a virtual platform for medical scenarios, enabling learners to diagnose, treat, and make decisions in a controlled digital environment.
4. Task Trainers: Specific skills, such as suturing or lumbar punctures, can be honed using task trainers—simplified models designed for targeted practice.
Benefits of Simulation-Based Healthcare Education:
1. Risk-Free Learning: Simulation allows learners to make mistakes and learn from them without compromising patient safety. This risk-free environment fosters confidence and competence.
2. Reproducibility: Simulations can be repeated, ensuring consistent exposure to critical scenarios. This reproducibility is crucial for skill mastery and proficiency.
3. Interdisciplinary Training: Healthcare is a collaborative field. Simulation models provide a platform for interdisciplinary training, allowing various professionals to work together in simulated patient care.
4. Customized Learning Paths: Learners can tailor their educational experience by choosing specific scenarios, repetition levels, and difficulty levels. This customization caters to individual learning styles.
5. Objective Assessment: Simulation-based assessments offer objective metrics for evaluating learners' performance. This data-driven approach enhances transparency and fairness in evaluations.
Applications Across Healthcare Professions:
1. Medical Students: Simulation models supplement traditional medical training, offering hands-on experiences that bridge the gap between theory and practice. Students can refine their clinical skills in a controlled setting before entering real patient care environments.
2. Nursing Education: Nurses benefit from simulation training to enhance their clinical skills, critical thinking, and decision-making abilities. Simulated scenarios range from routine patient care to emergency situations.
3. Surgical Training: Surgeons use high-fidelity simulators and VR platforms for procedural practice, enabling them to refine techniques and adapt to new technologies before performing surgeries on real patients.
4. Emergency Medicine: Simulations prepare emergency responders and physicians for high-stakes situations, such as trauma care or mass casualty incidents. These scenarios enhance preparedness and coordination.
5. Pharmacy and Allied Health Professions: From medication administration to patient counselling, simulation models offer a versatile platform for pharmacy and allied health education.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the integration of simulation in healthcare education is promising, challenges persist. High initial costs, faculty training, and the need for continuous technological updates pose barriers. However, ongoing advancements in technology, increased collaboration between educators and industry experts, and a growing awareness of the benefits are driving positive change.
The future of healthcare education through simulation models holds exciting possibilities
1. Personalized Learning Experiences: AI-driven simulations may adapt to individual learners, providing personalized training experiences based on strengths, weaknesses, and learning preferences.
2. Global Collaboration: Virtual simulations can facilitate global collaborations, allowing learners from different parts of the world to engage in shared educational experiences, and fostering cultural competence.
3. Telemedicine Simulations: With the rise of telehealth, simulations may focus on telemedicine scenarios, preparing healthcare professionals for virtual patient interactions and remote diagnostics.
4. Incorporation of Big Data: Analytics from simulation sessions can contribute to big data repositories, offering valuable insights into learning patterns, areas of improvement, and trends across healthcare education.
The future of healthcare education is undeniably intertwined with the evolution of simulation models. As technology continues to advance and educators embrace innovative approaches, learners across various healthcare professions stand to benefit from immersive, realistic training experiences. While challenges persist, the trajectory is clear—simulation-based education is not just a trend but a transformative force shaping the next generation of competent and compassionate healthcare professionals
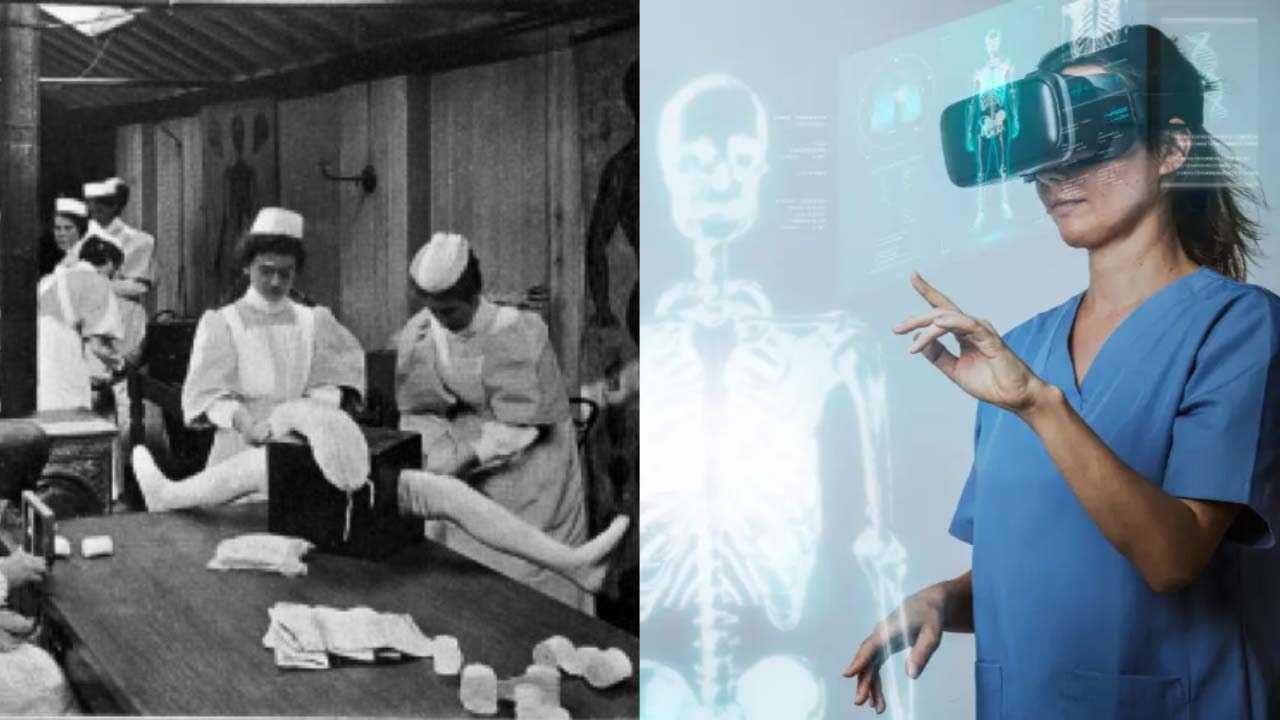
 The future of healthcare education is undeniably intertwined with the evolution of simulation models. As technology continues to advance and educators embrace innovative approaches, learners across various healthcare professions stand to benefit from immersive, realistic training experiences.
The future of healthcare education is undeniably intertwined with the evolution of simulation models. As technology continues to advance and educators embrace innovative approaches, learners across various healthcare professions stand to benefit from immersive, realistic training experiences.










.jpeg)











.jpg)