Fluorosis is a crippling disease resulting from the deposition of fluorides in the hard and soft tissues of the body due to excess intake of fluoride through drinking water/food products/industrial pollutants over a long period. It results in dental fluorosis, skeletal fluorosis, and non-skeletal fluorosis. Easy detection of fluorides in water can help preventing the public health hazards.
Scientists from the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, have developed an equipment-free fluoride ion detection and quantification in drinking water with the naked-eye. It can be operated by non-experts for household use to evade Fluorosis-based disorders.
The technology developed by Dr. Jayamurugan Govindasamy and his team involves a push-pull chromophore based on 2,3-disubstituted 1,1,4,4-tetracyano-1,3-butadienes (TCBDs) that changes color upon exposure to fluoride ion. The identified chromophore (C3-phenyl, C2-urea functionalized TCBD) is the result of a systematic study seeded by the Early Career Research (ECR) Award and further supported by the Ramanujan Fellowship grant of DST received by Dr. Govindasamy. The results were recently published in the Journal of Organic Chemistry. The researchers designed urea as an unusual donating moiety instead of traditional donor moieties, such as amines, to obtain better optoelectronic properties. The charge-transfer (CT) property that arises through-bond in aniline donor is usually quenched due to a photoinduced electron transfer (PET) mechanism. Whereas upon introducing urea as an electron donor, the CT exhibited both spaces as well as through bond due to “Field-effect”. Thus partial overcoming of the PET process, which led to white light emission.
Later, they extended its applicability in sensing of biologically relevant fluoride, as it is well known that fluoride can bind with urea via H-bonding interaction. Thus the combination of the push-pull chromophore with urea turned out to be an ideal system for the same. The INST scientists have optimized the synthesis of this chromophore in the laboratory scale
Furthermore, the design and synthesis can be slightly modulated to increase the sensitivity from 3 ppm to less than 1 ppm. Currently, the INST team is working in this direction. The major cost involves only the synthesis of the chromophore, making it affordable and accessible.
Although a vast number of reports are available for chromogenic and chromo-fluorogenic receptors in solution, only a limited number of reports which studied solid-phase detection. However, all those receptors suffer some drawbacks such as they generally exhibit color change only in organic medium and inorganic fluoride source, competing for affinity towards other anions such as acetate and phosphate, with a relatively high minimum detection limit of 10–30 ppm, work only with concentrated HCl, use of metals, delayed response, etc. while some works only with UV-lamp and chemically treated paper.
The non-planar push-pull chromophores sense fluoride ion with the naked eye in both solutions- as well as solid-phases.
The invention has been protected by filing the patent (202011028595). This work was supported by DST-SERB through the Early Career Research Award and Ramanujan Fellowship to Dr. JayamuruganGovindasamy.
Several companies sell solution-based photometric as well as colorimetric sensor kit, including few Indian companies. However, there is no single product based on low-cost paper-strip available to bring down the cost of the kit as well as easy handling by a layman.
Currently, one German company sells a paper-strip test kit for the detection of HF with a sensitivity of up to 20 ppm that too works only with hydrochloric acid (pH<1). This kit developed by INST can be used by a non-expert, with high sensitivity up to 3 ppm in aqueous/DMSO 1:1 condition and with only DMSO up to 1 ppm and free of dangerous chemicals and equipment.
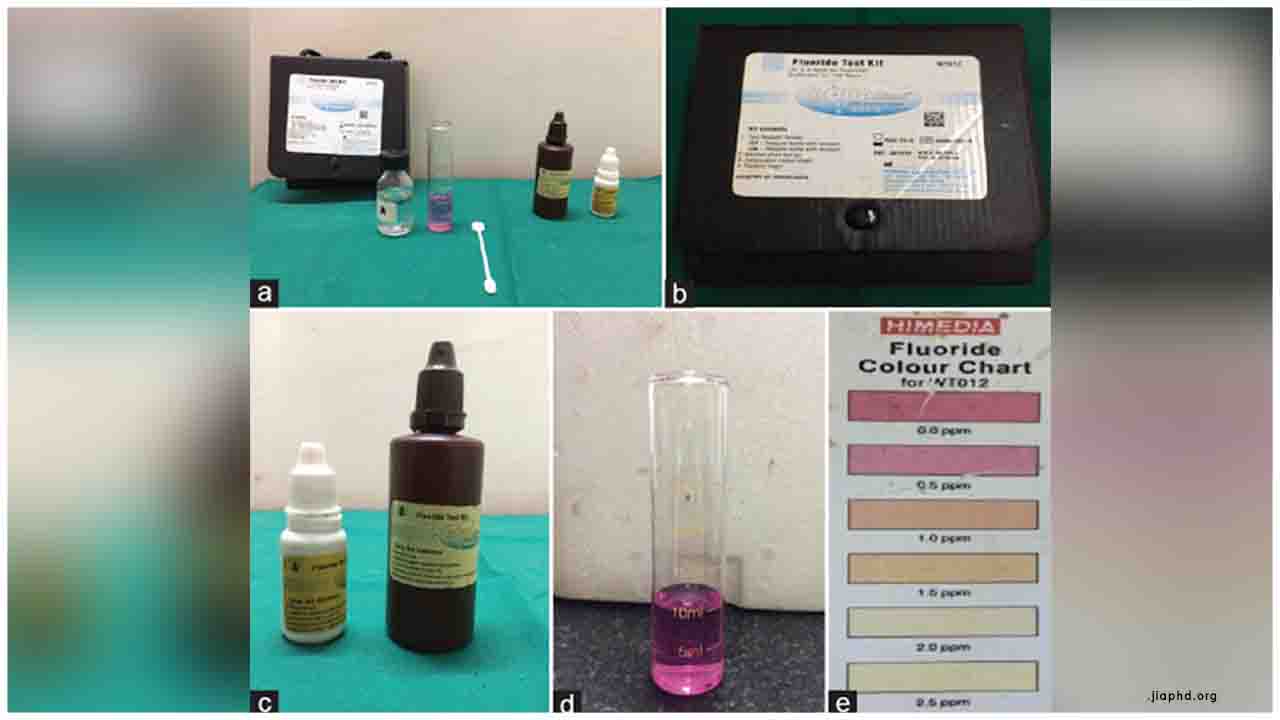
 Equipment-free, a simple paper-strip based naked-eye fluoride ion detection and quantification kit in drinking water to evade Fluorosis-based disorders
Equipment-free, a simple paper-strip based naked-eye fluoride ion detection and quantification kit in drinking water to evade Fluorosis-based disorders











.jpeg)

.jpeg)






.jpeg)










.jpg)