India stands on the cusp of a healthcare revolution, driven by the rapid rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI). Experts forecast that by 2025, AI will contribute between USD 25 to 30 billion to the country’s GDP, marking a seismic shift in how medical services are delivered. As technology advances, the potential to improve diagnostics, treatment, and accessibility is immense but only if India can overcome a maze of regulatory, infrastructural, and talent-related challenges.
In a landscape where digital transformation is sweeping through almost every sector, the healthcare industry is no exception. Recent reports highlight that AI-powered solutions have already outpaced their adoption in sectors like FMCG and manufacturing. The progress in healthcare is promising, yet critics warn that the pace still lags behind more mature industries like banking and finance. The key question remains: Can India harness AI to build a more efficient, patient-centric healthcare system that benefits millions across urban and rural areas alike?
Imagine a future where diagnosing diseases happens in minutes rather than days. Envision hospitals where cutting-edge AI tools analyse medical images, flagging potential issues long before symptoms arise. This isn’t a scene from a sci-fi movie it is the emerging reality of Indian healthcare. With government-led initiatives such as the IndiaAI Mission and robust legislation like the Digital Personal Data Protection Act of 2023, the country is laying the groundwork for a digitally empowered healthcare ecosystem.
These government initiatives are designed to ensure that the integration of AI into healthcare is both responsible and secure. By protecting personal data and fostering innovation, these policies aim to build a system where advanced technology can thrive without compromising patient safety or privacy.
India’s healthcare market has long been recognized for its role as a global supplier of generic medicines and medical services. Yet, with the advent of AI, the industry is poised to move far beyond its traditional strengths. Recent estimates suggest that the integration of AI could propel the sector into a new league potentially adding up to USD 30 billion to India’s economy by 2025. This growth is not merely an increase in numbers; it represents a fundamental shift in how healthcare services are conceived, delivered, and scaled.
One of the driving forces behind this transformation is the massive surge in AI adoption in medical settings. In recent years, over 40% of healthcare providers have integrated some form of AI into their operations. This rapid adoption rate surpasses that of other sectors such as FMCG and manufacturing, reflecting the transformative impact AI is expected to have on patient care.
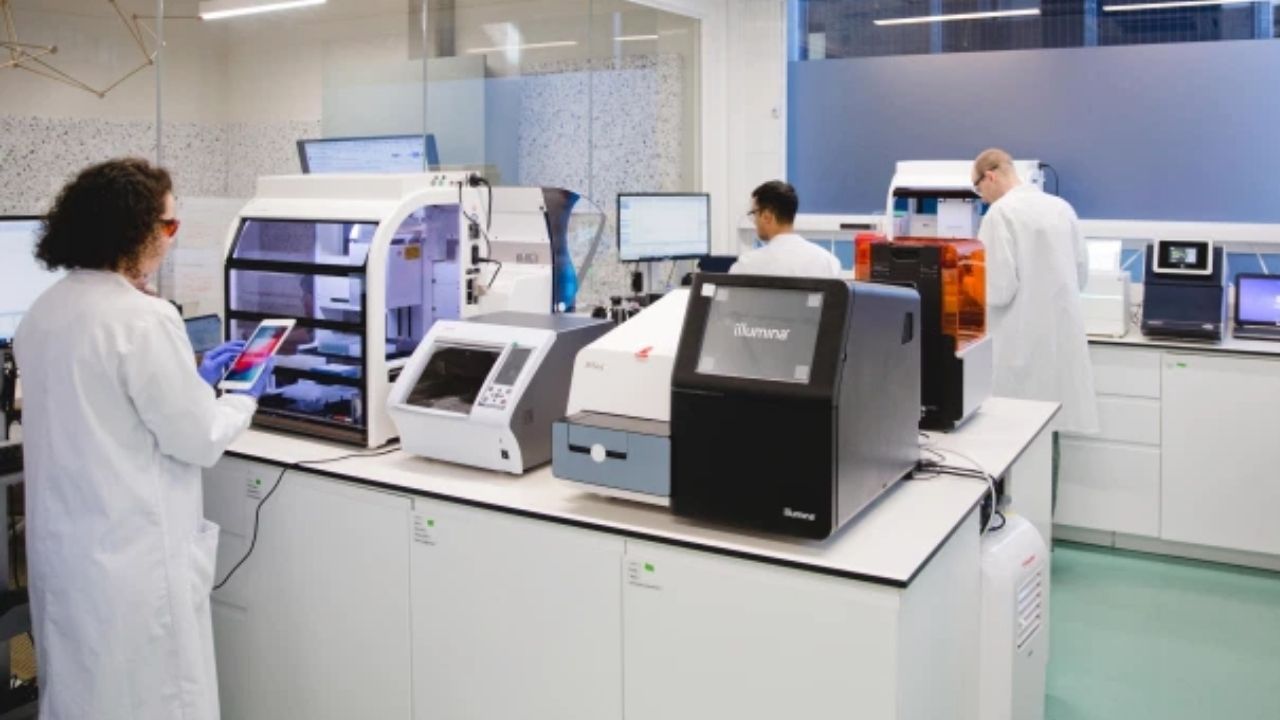
At the heart of the AI revolution in healthcare is the promise of improved diagnostics. AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data from medical imaging and electronic health records to detect diseases at their earliest stages. This Is particularly crucial in conditions where early detection can mean the difference between life and death cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes, to name a few.
For example, AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyse X-rays and MRIs with remarkable accuracy, often identifying subtle patterns that human eyes might miss. In a country as populous as India, where millions seek medical care daily, such precision can lead to earlier interventions, reducing treatment costs and improving outcomes.
Additionally, digital health records, powered by AI, can streamline the entire patient journey from diagnosis to treatment by ensuring that accurate, up-to-date information is available to doctors at every step. This seamless integration of technology into healthcare can minimize errors, speed up diagnoses, and ultimately save lives.
The ripple effects of AI adoption extend beyond patient care and diagnostics. The digital transformation of healthcare is also expected to impact India’s export market. Recent data shows that India’s surgical consumables and disposables exports reached USD 1.6 billion in the fiscal year 2022-23. While the country has cemented its reputation as a global supplier of generic drugs, it still depends on imports for high-tech medical equipment. Strengthening the domestic manufacturing base for such technologies is critical for long-term sustainability.
Targeted investments in state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, workforce training, and research can transform India into a fully self-reliant healthcare hub. With AI-driven systems reducing administrative and operational delays, Indian pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturers can boost their productivity and quality, making the country a magnet for global investments.
Despite the tremendous potential, several challenges threaten to slow down the integration of AI into healthcare. One of the most significant hurdles is the current regulatory framework. India’s drug regulators and healthcare authorities have been criticized for slow, cumbersome processes that stifle innovation. For instance, the lengthy approval times for exporting raw materials and issuing manufacturing licenses create delays that can hinder growth.
Regulatory fragmentation is another key issue. In many rural areas, where digital infrastructure is still evolving, ensuring data security and consistent application of policies becomes a daunting task. These challenges are compounded by a shortage of professionals trained in the nuances of AI. With an ever-growing reliance on digital tools, there is an urgent need for specialized training programs that equip healthcare professionals with the skills needed to operate and maintain advanced AI systems.
To address these issues, policymakers must undertake comprehensive reforms aimed at streamlining processes, enhancing digital infrastructure, and fostering a culture of continuous learning within the healthcare sector. Establishing a centralized digital platform that integrates data from all regulatory agencies can also expedite approvals and improve transparency.
The future of AI-powered healthcare in India hinges on strategic investments and focused policy reforms. The government, along with private sector players, must commit to robust funding in key areas:
1. Enhancing Digital Infrastructure: Developing a secure, nationwide digital healthcare network is essential. This network should not only store electronic health records but also support real-time monitoring of patient data, enabling AI systems to function optimally. Investments in high-speed internet and advanced computing resources will be crucial, especially in rural areas that currently lag behind urban centers.
2. Cultivating Workforce Development: With a gap in specialized training, there is a pressing need to educate healthcare professionals in AI technologies. Government-backed training programs and partnerships with academic institutions can create a pipeline of skilled workers who can drive the digital transformation of healthcare. Continuous professional development in AI and digital tools should become a standard part of medical education.
3. Strengthening Domestic Manufacturing: To reduce dependence on imported high-tech medical equipment, India must bolster its domestic manufacturing capabilities. Incentivizing local production through tax breaks, grants, and easier regulatory procedures can help establish a robust ecosystem for medical technology. This, in turn, will not only meet domestic needs but also position India as a leading exporter in the global market.
4. Streamlining Regulatory Processes: As part of the digital transformation, regulatory agencies must adopt streamlined processes that are transparent, efficient, and adaptive. Creating a single-window clearance system for drug approvals, export licenses, and medical device certifications can reduce delays and foster a more business-friendly environment. Simplified regulations will help attract further foreign investment, contributing to the overall growth of the sector.
The Indian government is already making strides toward creating a digitally empowered healthcare ecosystem. Initiatives such as the IndiaAI Mission and the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, are key components of this strategy. These policies aim to safeguard patient data while promoting innovation, ensuring that the benefits of AI can be realized without compromising privacy or security.
Moreover, the government’s focus on promoting medical tourism and public-private partnerships in healthcare signals a broader commitment to transforming the sector. By encouraging investments in both infrastructure and technology, India is positioning itself as a global leader in affordable, high-quality healthcare.
Recent reports indicate that AI adoption in healthcare has surpassed its use in other major sectors such as FMCG and manufacturing. This rapid uptake reflects the immense potential of digital technologies to transform patient care, streamline operations, and drive down costs. As more hospitals and clinics integrate AI-driven solutions into their daily practices, the competitive advantage will increasingly lie with those who can harness these innovations effectively.
For instance, AI-powered diagnostic tools are not only speeding up the detection of diseases but also enhancing the accuracy of treatments. Digital health records allow for seamless sharing of patient information among healthcare providers, reducing errors and improving overall outcomes. As these technologies become more widespread, the benefits will extend far beyond individual hospitals, transforming the entire healthcare ecosystem.
Despite the promising prospects, the journey toward a fully integrated AI-powered healthcare system is fraught with challenges. Several obstacles must be overcome to fully unlock the potential of digital health:
1. Regulatory Fragmentation: India’s regulatory environment is complex and often fragmented, which can hinder the swift implementation of new technologies. Aligning policies across different states and sectors requires coordination and a unified vision a task that is easier said than done.
2. Workforce Training Deficits: The shortage of professionals trained in AI is a significant barrier. As the healthcare sector becomes increasingly digitized, there is a critical need for educational programs that can equip doctors, technicians, and administrators with the skills required to manage and operate AI systems.
3. Infrastructure Limitations in Rural Areas: While urban centers are rapidly adopting digital healthcare solutions, rural areas continue to face challenges such as poor internet connectivity and inadequate technological infrastructure. Bridging this gap is essential for ensuring that all citizens, regardless of location, benefit from advancements in healthcare.
4. Data Security Concerns: As more patient data is digitized, concerns about privacy and security become paramount. Robust data protection measures must be put in place to build trust among patients and healthcare providers, ensuring that sensitive information is safeguarded against breaches and misuse.
5. Dependence on Imports for High-Tech Equipment: India has made significant progress in generic drug manufacturing, but it still relies heavily on imports for high-tech medical devices. Building a stronger domestic manufacturing base for advanced technologies is critical for long-term self-reliance and economic growth in the healthcare sector.
To overcome these challenges and fully capitalize on the opportunities, a multi-pronged approach is necessary:
A. Policy Reforms and Regulatory Overhaul
Centralized Approval Systems: Establishing a unified, digital platform for drug and device approvals can drastically reduce bureaucratic delays. A single-window clearance system would allow for faster processing and better oversight.
Harmonized Regulations: Aligning state and central regulations ensures consistency and reduces the administrative burden on healthcare providers. This harmonization is key to creating an environment conducive to innovation.
B. Investment in Infrastructure and Workforce Development
Enhanced Digital Infrastructure: Investing in high-speed internet and advanced computing capabilities, particularly in rural areas, will ensure that AI tools can be deployed effectively across the country.
Specialized Training Programs: Collaboration between government, industry, and educational institutions can create comprehensive training programs focused on AI in healthcare. This will equip the workforce with the necessary skills and reduce the current talent gap.
C. Encouraging Domestic Manufacturing
Incentives for Local Production: Offering tax breaks, subsidies, and easier regulatory processes can boost domestic production of high-tech medical equipment. This not only reduces reliance on imports but also strengthens the local economy.
Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between the government and private enterprises can drive innovation and ensure that new technologies are developed and scaled efficiently. Such partnerships have the potential to revolutionize the healthcare sector by combining public oversight with private sector efficiency.
D. Strengthening Data Security and Privacy Measures
Robust Digital Protection Frameworks: Implementing stringent data security protocols is essential for protecting patient information. Investments in cybersecurity infrastructure and continuous monitoring will build trust in digital healthcare systems.
Compliance with Global Standards: Aligning data protection policies with international standards will help Indian healthcare providers meet global benchmarks, making the industry more attractive to foreign investors and partners.
D. Promoting Awareness and Adoption
Industry Conferences and Workshops: Regular forums where healthcare professionals can share best practices, learn about new AI technologies, and discuss regulatory challenges will foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating patients about the benefits of digital health and AI can drive demand for advanced services, creating a positive feedback loop that encourages further investments in technology.
India’s transformation of its healthcare sector through AI adoption has implications far beyond its borders. As one of the world’s largest suppliers of generic medicines, India plays a crucial role in global health. The successful integration of AI can not only improve the quality and efficiency of healthcare in India but also set a benchmark for other developing nations.
By positioning itself as a leader in AI-powered healthcare, India can tap into new markets and strengthen its export potential. The digital transformation will help reduce costs, improve patient outcomes, and make advanced medical care more accessible. International pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers are increasingly looking to diversify their supply chains, and a modernized, efficient Indian healthcare system could become their preferred partner.
The road ahead for India’s healthcare sector is both challenging and filled with promise. With projected contributions of USD 25-30 billion to the GDP by 2025 from AI in healthcare alone, the potential benefits are enormous. As the digital transformation accelerates, traditional sectors like FMCG and manufacturing may find themselves overshadowed by the rapid advancements in medical technology.
For patients, this shift means better diagnostic accuracy, personalized treatment plans, and improved access to healthcare services even in remote areas. Digital health records, AI-powered diagnostic tools, and telemedicine will become integral parts of everyday medical care. As a result, healthcare will be faster, more efficient, and more responsive to individual needs.
For healthcare providers, the integration of AI means a chance to focus on patient care rather than administrative burdens. With streamlined processes and enhanced data analytics, doctors can spend more time on diagnosis and treatment, leading to better outcomes. In turn, this will boost the overall efficiency of the healthcare system and reduce costs.
For investors, the transformation of the healthcare sector into a digitally advanced ecosystem represents a golden opportunity. With improved regulatory processes, robust digital infrastructure, and a strong focus on innovation, India’s healthcare market is poised for explosive growth. As global investors look to tap into emerging markets, India’s commitment to digital healthcare will undoubtedly attract significant capital, further fueling the sector’s expansion.
Beyond the economics and technology, the true promise of AI in healthcare lies in its ability to improve lives. In a country where millions struggle with limited access to quality healthcare, digital transformation can be a game-changer. AI-driven tools can help bridge the gap between urban and rural healthcare, ensuring that even the most remote communities receive timely and accurate medical care.
Imagine a scenario where a patient in a small village can receive a diagnosis from a top specialist in a metropolitan hospital via telemedicine, or where a rural clinic uses AI to quickly and accurately interpret complex medical tests. This is not a distant dream but a reality that is rapidly approaching. By using AI, India can overcome many of the traditional barriers to healthcare access, such as geographical isolation and limited resources.
Furthermore, improving healthcare outcomes has a cascading effect on society. Better health leads to increased productivity, reduced healthcare costs, and a higher quality of life. As more people receive timely and effective treatment, the nation’s overall economic and social well-being will improve, creating a positive cycle of growth and development.
For India to fully realize the benefits of AI in healthcare, a concerted effort is required from all stakeholders. Policymakers must implement reforms that streamline regulatory processes and promote innovation. Investments in digital infrastructure, workforce training, and domestic manufacturing are critical to building a resilient healthcare system. At the same time, public-private partnerships can drive the necessary innovation and ensure that new technologies are effectively integrated into clinical practice.
Healthcare providers must also embrace change by adopting digital tools and refining their practices to leverage AI’s full potential. Continuous education and training in digital technologies are essential for doctors and support staff to keep pace with the rapid advancements in the field.
Finally, the public must be educated about the benefits of digital healthcare. Transparency and clear communication can build trust in AI-driven systems, encouraging broader adoption and ensuring that patients understand how these technologies can improve their care.
India’s journey toward a digitally empowered healthcare system is well underway. With a projected contribution of up to USD 30 billion to the GDP by 2025, the integration of AI into healthcare is not just an economic opportunity; it is a vital step toward creating a more equitable, efficient, and patient-focused medical ecosystem.
As we moves forward, the integration of AI in healthcare must be pursued with urgency, transparency, and a commitment to innovation. The journey ahead is challenging, but the rewards, a healthier, more prosperous nation are well worth the effort.

 The integration of AI into healthcare is not just an economic opportunity; it is a vital step toward creating a more equitable, efficient, and patient-focused medical ecosystem.
The integration of AI into healthcare is not just an economic opportunity; it is a vital step toward creating a more equitable, efficient, and patient-focused medical ecosystem.
















.jpeg)


.jpeg)



.jpeg)
.jpeg)






.jpeg)





