In a recent revelation by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), startling findings have emerged regarding the quality and completeness of prescriptions issued by doctors across tertiary care hospitals in India. The study, published in the Indian Journal of Medical Research (IJMR), sheds light on the prevalence of incomplete and deviant prescriptions, raising concerns about patient safety and healthcare efficacy.
ICMR’s Prescription Analysis: The ICMR study, titled ‘Evaluation of prescriptions from tertiary care hospitals across India for deviations from treatment guidelines & their potential consequences’, was conducted between 2019 and 2020. The survey encompassed outpatient departments of renowned government hospitals, including Delhi AIIMS and Safdarjung Hospital, under the supervision of 13 ICMR Rational Use of Medicines Centres.
Key Findings and Prescription Deviations: Out of a total of 7,800 patients prescriptions analysed, the study identified significant deficiencies in 2,171 prescriptions. Alarmingly, around 45% of doctors prescriptions were deemed incomplete, lacking critical details such as formulation, dose, duration, and frequency. Moreover, approximately 10% of the examined prescriptions exhibited “unacceptable deviations,” including inappropriate medication prescriptions and the assignment of more than one diagnosis.
Understanding Unacceptable Deviations: An “unacceptable deviation” in a prescription is characterized by its potential consequences, ranging from drug interactions and adverse drug reactions (ADRs) to increased treatment costs and antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Such deviations undermine patient safety and pose challenges to effective healthcare delivery.
Common Prescription Errors and Their Implications: The study highlighted several recurring prescription errors and their implications on patient health:
1. Inappropriate Medications: Patients with conditions like upper respiratory tract infections (URTI) and high blood pressure received inappropriate prescriptions, contributing to potential treatment inefficacy and adverse reactions.
2. Rational Use of Gastroprotective Drugs: Prescriptions lacking gastroprotective drugs in patients at risk of developing peptic ulcers pose significant risks, including abdominal bloating and potential ulcer development.
3. Questionable Use of Specific Medications: The study flagged the unnecessary use of medications like trypsin/chymotrypsin and serratiopeptidase without sufficient scientific evidence to support their efficacy.
4. Concerns with Fixed-Dose Combinations (FDCs): The co-prescription of FDCs, such as amoxicillin plus clavulanic acid, in URTIs can contribute to antimicrobial resistance (AMR) over time, compromising the effectiveness of antibiotics.
Physician Compliance with ICMR Guidelines: Despite these findings, the study noted that a majority of physicians (around 55%) adhered to disease-specific ICMR guidelines, highlighting the importance of standardized treatment protocols in optimizing patient outcomes and reducing prescription deviations.
Implications for Patient Care and Healthcare System: The implications of incomplete and deviant prescriptions extend beyond individual patient experiences to broader healthcare system challenges. Addressing prescription discrepancies is critical for enhancing patient safety, optimizing treatment outcomes, and mitigating the risks associated with inappropriate medication use.
Addressing Prescription Quality: In conclusion, the ICMR study showcased the importance of ensuring prescription quality and adherence to standardized treatment guidelines in healthcare delivery. By identifying and rectifying prescription deviations, healthcare providers can enhance patient care, minimize treatment risks, and uphold the principles of evidence-based medicine in clinical practice. The study’s findings serve as a call to action for continuous quality improvement initiatives aimed at optimizing prescription practices and promoting patient-centered care in India’s healthcare landscape.
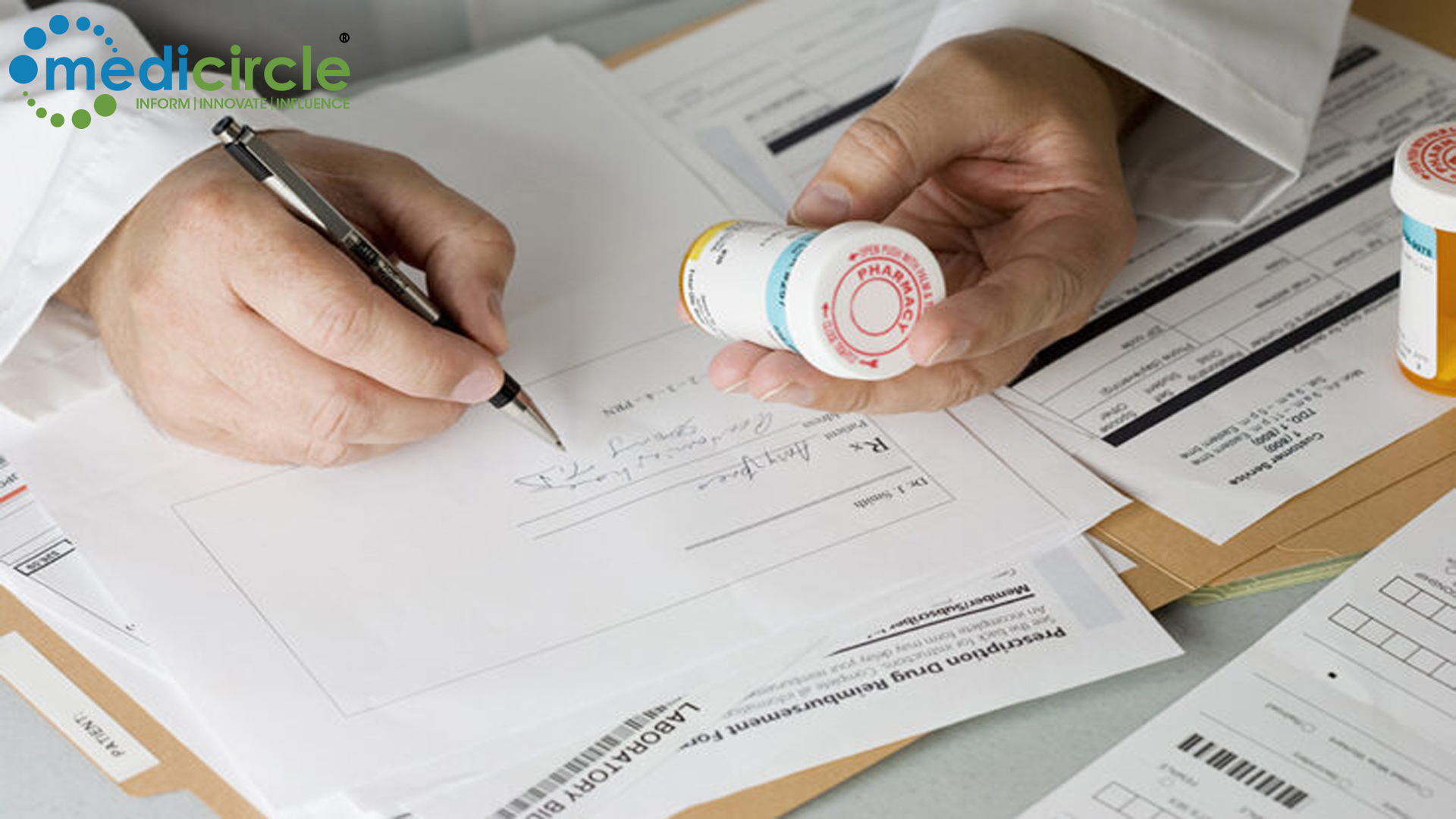

 The implications of incomplete and deviant prescriptions extend beyond individual patient experiences to broader healthcare system challenges.
The implications of incomplete and deviant prescriptions extend beyond individual patient experiences to broader healthcare system challenges.

















.jpeg)

.jpeg)










.jpg)




.jpg)

