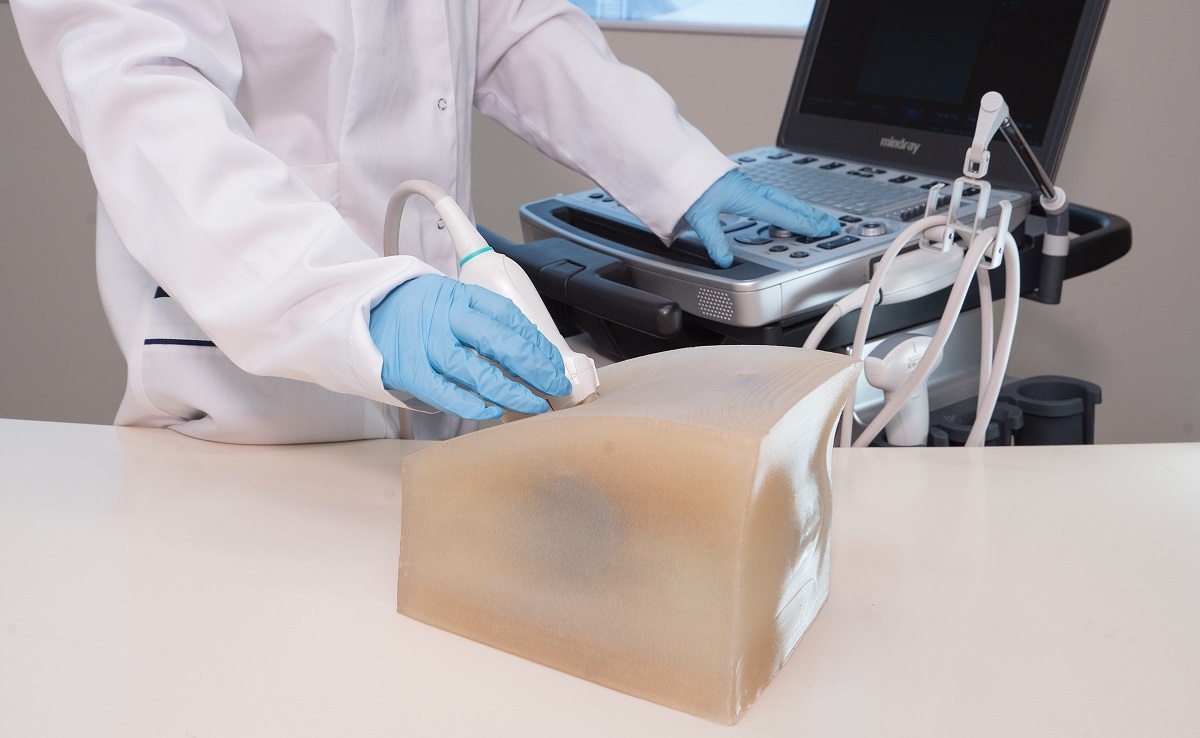
Scientists in Moscow have successfully developed Russia's first lumbar spine phantom. This model will enable anesthesiologists to practice needle insertion techniques under ultrasound guidance, ensuring a safe and effective training environment devoid of any risk to patients during and after procedures aimed at treating chronic pain. Yuri Vasilev, the Chief Consultant for Radiology and CEO of the Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine within the capital's Department of Healthcare, made this announcement.
"We are committed to enhancing the quality of medical care for patients. The scientists at the Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine have successfully developed Russia's first lumbar spine phantom for anesthesiology. This model facilitates the practice of anesthetic drug administration techniques without endangering patients. The uniqueness of these phantoms lies in their design for training medical professionals in ultrasound-guided procedures, making it vital to accurately mimic the ultrasound image during fabrication. Since last year, Moscow has initiated small-scale production of anatomical models for physician training," stated Vasilev.
The in-house-produced phantoms stand out from their foreign counterparts by offering better functionality, durability, and affordability, while being adaptable to the specific needs of different medical institutions.
"To create the phantom, our team utilized anonymized CT scans to produce a precise anatomical replica. The phantom is made from durable materials and represents a soft-tissue model of the spine. A key differentiator of our phantom is the inclusion of the sacrum, which allows for training in additional types of regional anesthesia techniques, such as caudal blocks. Our manufacturing process enables us to meet specific anatomical requirements and simulate various anatomical variations," explained Anton Vladzimirsky, Deputy Director for Research at the Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine.
Modern medical practitioners are using these phantoms to refine their skills. The models are currently being acquired by hospitals and simulation centers and are integral to training programs. As of now, small-scale production of these innovative training models has commenced at the Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine.
A total of six phantoms have been developed in the Centre's laboratory for training in ultrasound imaging skills. Among the recent innovations is a face phantom designed for cosmetic procedures. This model incorporates a skull, salivary glands, vascular structures, and skin, with varying densities and thicknesses of subcutaneous fat in specific regions. The simulator allows for repeated practice of injection techniques in areas such as the nasolabial folds, lips, forehead, and temples. Additionally, the Centre has created models of mammary and thyroid glands, a liver model, and a phantom mimicking human vessels and nerves for training in ultrasound diagnostic techniques.
The Centre for Diagnostics and Telemedicine is a premier scientific and practical organization within Moscow's social development framework, founded in 1996. It specializes in integrating artificial intelligence in medicine, advancing radiological diagnostics, optimizing departmental operations in healthcare institutions, conducting scientific research, and providing education for medical professionals.

 It specializes in integrating artificial intelligence in medicine, advancing radiological diagnostics, optimizing departmental operations in healthcare institutions, conducting scientific research, and providing education for medical professionals.
It specializes in integrating artificial intelligence in medicine, advancing radiological diagnostics, optimizing departmental operations in healthcare institutions, conducting scientific research, and providing education for medical professionals.










.jpeg)











.jpg)