In a recent breakthrough, researchers have developed a groundbreaking biochip that harnesses the power of electricity to accelerate wound healing. This innovative technology, developed by scientists from Chalmers University of Technology and the University of Freiburg, has the potential to revolutionize the way we treat wounds, offering hope to individuals suffering from chronic wounds, including those with diabetes.
You might be wondering how electricity could possibly help heal a wound. Well, it all stems from an old theory that suggests electrical stimulation can influence the healing process of our skin. The researchers at these universities explored this theory further and found that skin cells exhibit fascinating behaviour when exposed to electric fields. They tend to move in specific directions, a phenomenon known as "electrotaxis."
Building on this concept, the researchers created a biochip designed to utilize this electrotactic behaviour of skin cells. They conducted experiments on artificial test wounds using their chip, comparing wounds treated with electrical stimulation to those left untreated. The results were astonishing. Maria Asplund, the head of the research project, explained, "We were able to show that the old hypothesis about electric stimulation can be used to make wounds heal significantly faster. We stimulated one wound with an electric field, which clearly led to its healing three times as fast as the wound that healed without electric stimulation."
The implications of this discovery are immense. People suffering from chronic wounds, particularly those with diabetes, stand to benefit greatly from this novel form of treatment. Diabetes patients often experience slow wound healing, which can lead to severe complications and even death. Asplund stated, "We've looked at diabetes models of wounds and investigated whether our method could be effective even in those cases." The researchers found that electric stimulation significantly accelerated the healing process in diabetes-affected cells, bringing them closer to the healing rate of healthy skin cells.
The next phase of this groundbreaking research involves personalized treatments and a deeper exploration of how skin cells respond when healing less artificial wounds. Asplund expressed her vision for the future: "We are now looking at how different skin cells interact during stimulation, to take a step closer to a realistic wound." She also mentioned the possibility of creating a scan that can precisely determine the amount of stimulation needed for each individual's unique requirements.
Chronic wounds are a silent but significant societal issue, especially for those who suffer from conditions that impair their body's natural healing processes. Asplund emphasized the potential impact of their discovery, saying, "Our discovery of a method that may heal wounds up to three times faster can be a game-changer for diabetic and elderly people, among others, who often suffer greatly from wounds that won't heal."
In summary, the development of this electricity-powered biochip is a remarkable advancement in the field of wound healing. It has the potential to bring hope, relief, and faster healing to countless individuals dealing with chronic wounds, ultimately improving their quality of life and reducing the risk of complications. As researchers continue to refine this technology, it may indeed become a transformative tool in healthcare, offering new hope for those in need of faster and more effective wound healing
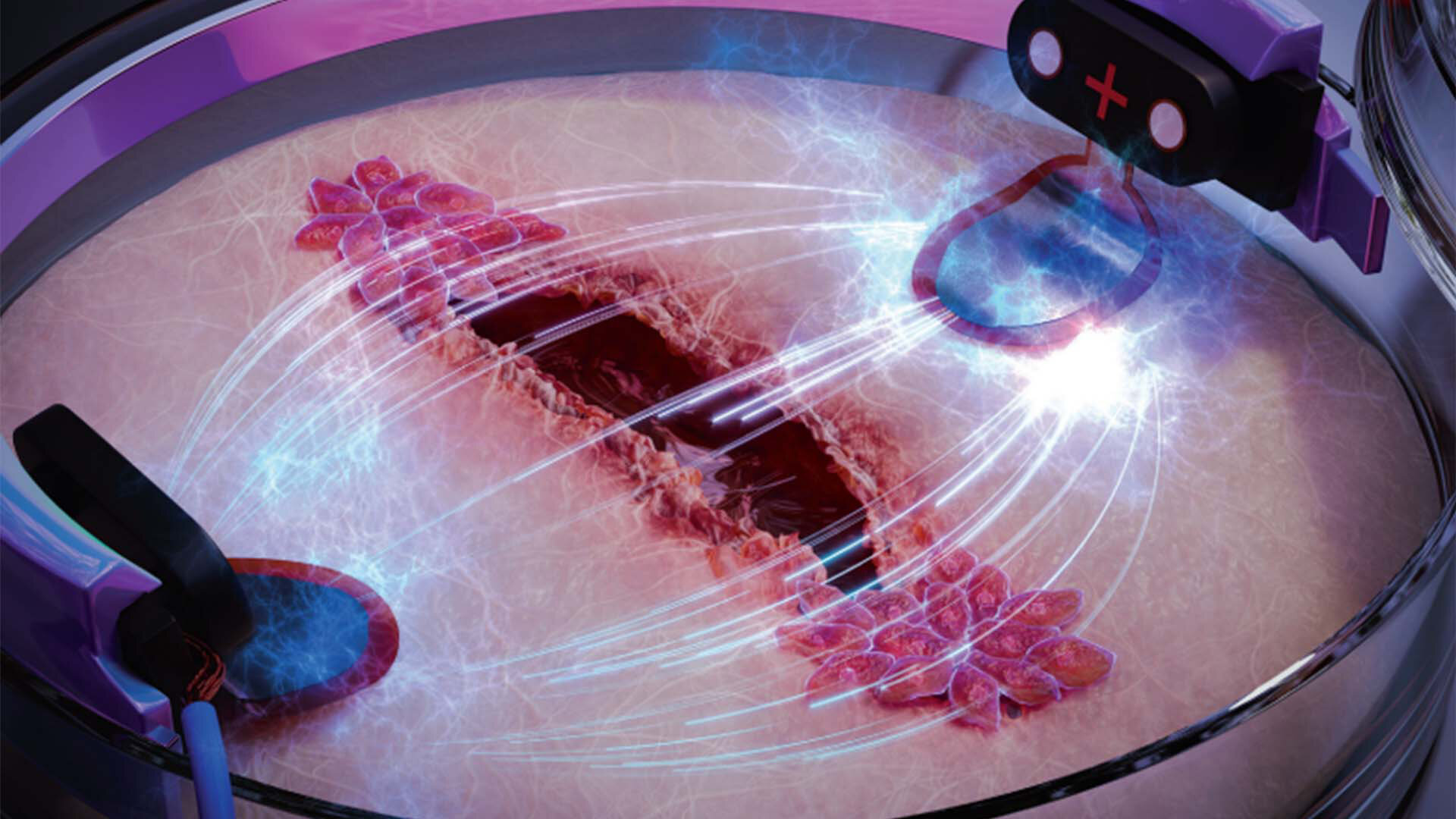
 The biochip, powered by electricity, is a significant advancement in wound healing, offering hope, relief, and faster healing for chronic wound patients, improving their quality of life.
The biochip, powered by electricity, is a significant advancement in wound healing, offering hope, relief, and faster healing for chronic wound patients, improving their quality of life.










.jpeg)











.jpg)