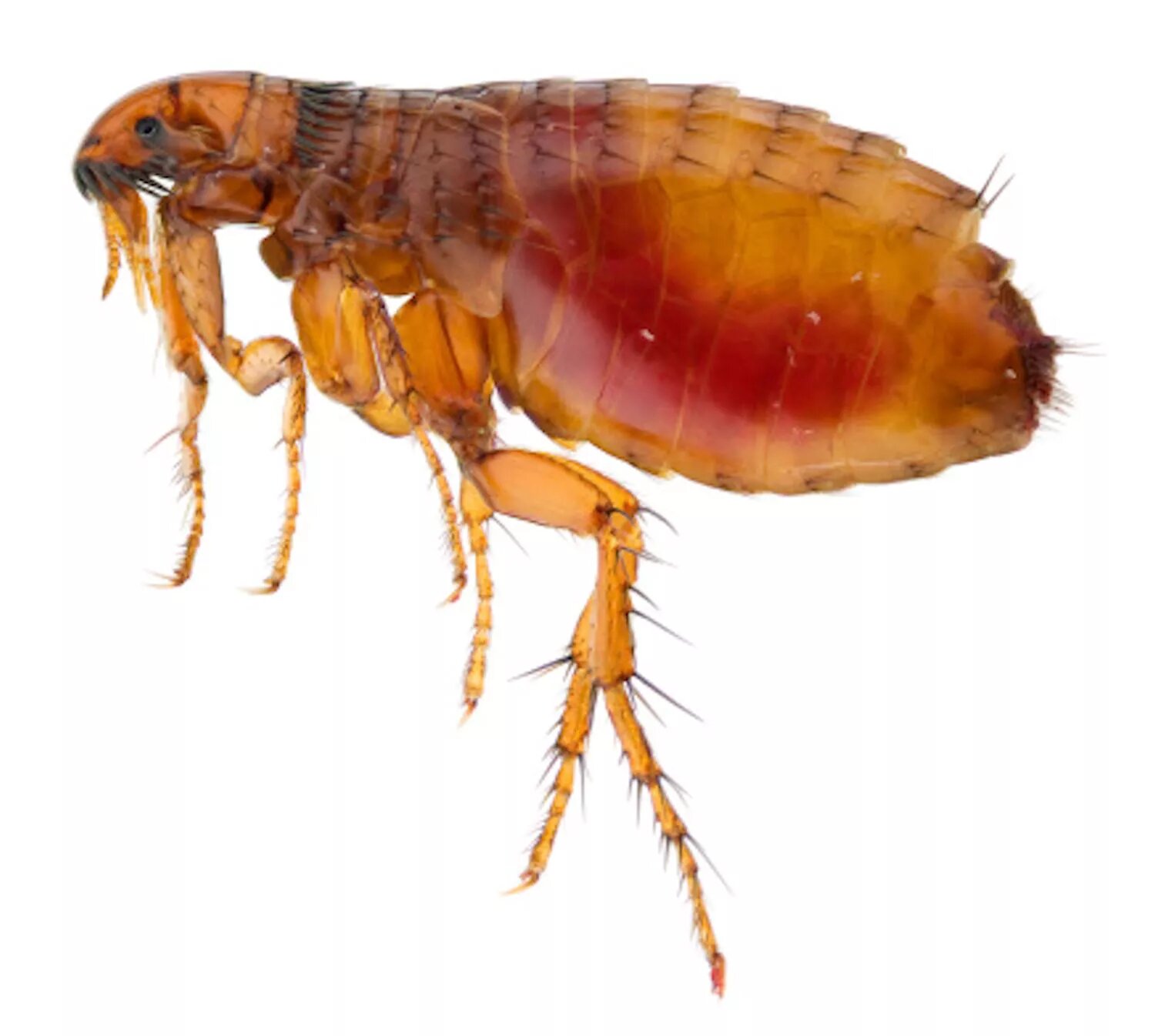
In the face of adversity, one man's struggle against a tiny flea bite serves as a stark reminder of the dangers posed by Typhus in India. Michael Kohlhof's battle for survival after contracting the disease has highlighted the urgent need to comprehend the menace of Typhus and take appropriate measures to combat its spread. This article sheds light on the flea-borne horror of Typhus, its prevalence in India, and the lessons we can learn from Michael Kohlhof's harrowing experience.
The Story of Michael Kohlhof:
Michael Kohlhof's ordeal began with a seemingly innocent flea bite. Little did he know that this unassuming insect would be the bearer of a life-threatening infection. The bacteria transmitted by the flea entered Michael's bloodstream, unleashing a series of symptoms that eventually led to a life-altering situation that forced him to amputate both his hands and parts of his feet.
Causes of Typhus:
Bacteria Carried by Infected Fleas: Typhus is caused by specific bacteria carried by fleas. When infected fleas bite humans, the bacteria enter the bloodstream, leading to the development of the disease.
Poor Hygiene and Overcrowding: Typhus is often prevalent in places with inadequate sanitation and overcrowded living conditions. Such environments create a breeding ground for fleas, increasing the risk of transmission.
Contact with Infected Individuals: Close contact with a person already infected with Typhus can also spread the disease.
Flea-Infested Animals: Besides humans, Typhus can also be transmitted through contact with animals like rats, dogs and cats, which are infested with infected fleas.
Lack of Vaccination: In areas where vaccinations against Typhus are not available, the risk of contracting the disease is higher.
Symptoms of Typhus:
High Fever: One of the primary indicators of Typhus is a persistent high fever that may reach up to 104°F (40°C) or even higher.
Body Aches and Rash: Patients with Typhus experience severe body aches and develop a characteristic rash, which begins as small red spots and later spreads across the body.
Headache and Chills: Intense headaches and chills are common symptoms of the disease, making the patient feel extremely unwell.
Fatigue and Weakness: Typhus often causes extreme tiredness and weakness, significantly reducing energy levels.
Delirium and Confusion: In severe cases, Typhus can lead to delirium and confusion, affecting the patient's mental state.
Prevalence of Typhus in India:
Typhus outbreaks have been reported in various parts of India. The disease tends to be more prevalent in regions with overcrowded living conditions and poor sanitation. India's vast population and the environmental factors in certain areas make it vulnerable to outbreaks of Typhus and other infectious diseases. Despite being a serious public health threat in India, it is uncertain how widespread and burdensome this disease is. The scarcity of statistical information and relevant health records on typhus in the outbreak region demonstrates that there is still a significant knowledge gap about this neglected illness.
Precautions against Typhus:
Maintain Clean and Hygienic Surroundings: Regular cleaning and proper waste disposal can reduce the flea population, minimizing the risk of Typhus.
Use Insect Repellents: When spending time outdoors, especially in flea-prone areas, apply insect repellents to prevent flea bites.
Avoid Contact with Infected Individuals: If you know someone has Typhus, avoid close contact to prevent transmission.
Protect Yourself from Flea-Infested Animals: Be cautious around animals that may carry infected fleas. Avoid handling them without proper protection.
Vaccination: In regions where Typhus is a concern, consider getting vaccinated to protect yourself from the disease.
Cure for Typhus:
Antibiotics: Typhus can be treated effectively with antibiotics, such as doxycycline or tetracycline, which help eliminate the bacteria causing the infection.
Supportive Care: Providing supportive care, such as fluids and medications to manage fever and pain, is crucial during the recovery process.
Hospitalization: Severe cases of Typhus may require hospitalization to ensure proper medical attention and management of complications.
Rest and Hydration: Rest and staying well-hydrated is essential for speedy recovery from Typhus.
Follow Medical Advice: Strictly adhere to the medical advice given by healthcare professionals to improve the chances of a full recovery.
Typhus is a severe disease that can have devastating consequences if not diagnosed and treated promptly. By understanding the causes, symptoms, precautions, and available cures for Typhus, individuals can take necessary steps to protect themselves and their communities from this potentially life-threatening infection. Remember, maintaining proper hygiene, avoiding flea-infested areas, and seeking medical attention when needed is essential in combating Typhus and preventing its spread.

 Typhus is a severe disease that can have devastating consequences if not diagnosed and treated promptly. By understanding the causes, symptoms, precautions, and available cures for Typhus, individuals can take necessary steps to protect themselves and their communities from this potentially life-threatening infection.
Typhus is a severe disease that can have devastating consequences if not diagnosed and treated promptly. By understanding the causes, symptoms, precautions, and available cures for Typhus, individuals can take necessary steps to protect themselves and their communities from this potentially life-threatening infection. 



















.jpeg)

.jpeg)










.jpg)




.jpg)

