A temporary switch to a restricted diet may lessen stress on your digestive system if you have diarrhea and possibly related symptoms like nausea, cramps in your stomach, and bloating. The diarrhea diet allows your bowels to recover while also assisting in the restoration of the fluid and electrolyte balance in your body.
Diarrhea, or loose, watery, and possibly more frequent bowel movements, is a common issue. It might be the only symptom or coexist with others like nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or weight loss. Fortunately, diarrhea typically lasts no longer than a few days.
Dietary recommendations for preventing diarrhea
- Idli/Idiyappam
- Curd rice
- Coconut water
- Lemon water
- Buttermilk
- Mint and honey/Cinnamon and honey drink.
- Banana
- Khichdi
- Soup and crackers
Foods to avoid while experiencing diarrhea
- Milk
- Fried, fatty, greasy foods
- Spicy foods
- Processed foods, especially those with additives
- Raw vegetables
- Onions
- Corn
- Fruits like pineapples, cherries, seeded berries, figs, currants, and grapes
- Alcohol
- Coffee, soda, and other caffeinated or carbonated drinks.
- Whole wheat, bran products, Shreddies, Mini Wheat, Raisin Wheat, Shredded Wheat, and Bran Flakes.
When experiencing diarrhea, every day consume 8 to 10 cups of fluid, such as water, broth, juice that has been diluted, weak tea, or electrolyte replacement drinks. Throughout the day, consume small, frequent meals slowly. To help firm up stools, look for sources of soluble fiber.
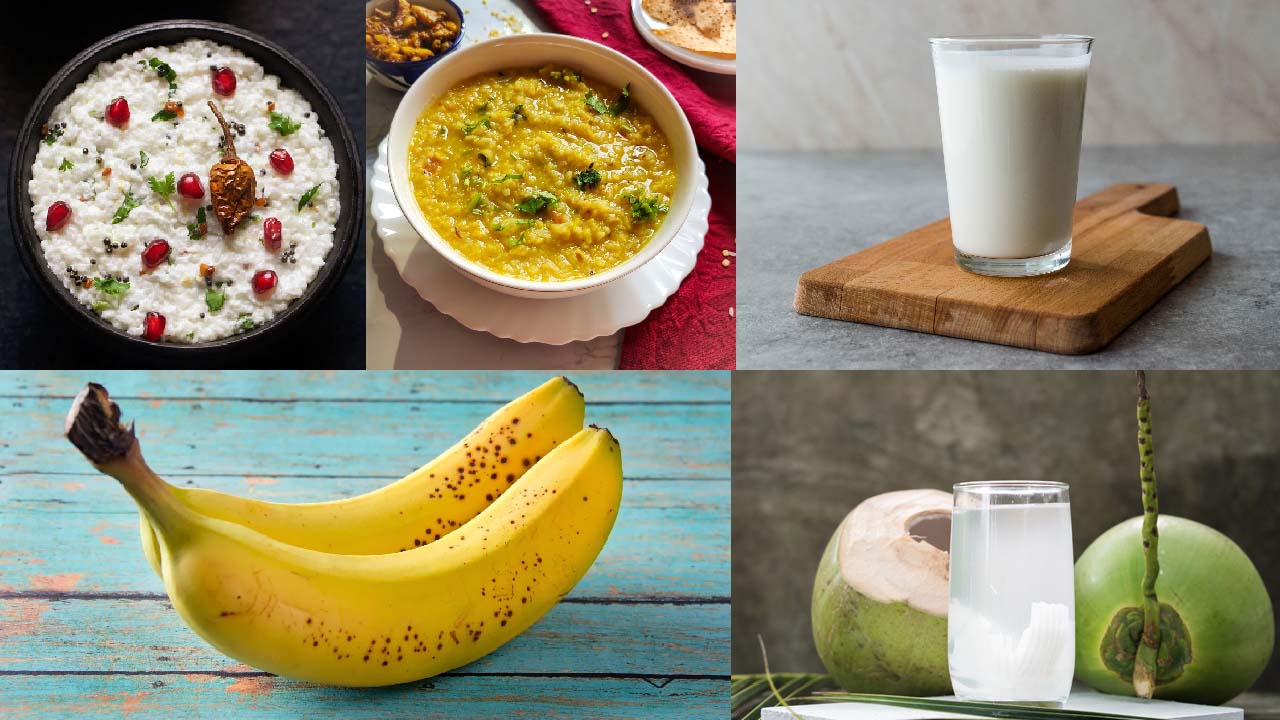

 Despite the fact that diarrhea is extremely common, it can still be dangerous. You can become extremely dehydrated when you have severe diarrhea, Here are some diet foods that you can consume when you have diarrhea.
Despite the fact that diarrhea is extremely common, it can still be dangerous. You can become extremely dehydrated when you have severe diarrhea, Here are some diet foods that you can consume when you have diarrhea.


















.jpeg)


.jpeg)



.jpeg)
.jpeg)






.jpeg)





