Monkeypox cases are on the rise. Monkeypox is commonly found in central and west Africa where there are tropical rainforests and where animals that may carry the virus typically live. But the cases are also being seen in countries where monkeypox is not endemic. Monkeypox is a disease caused by the monkeypox virus. The disease was first identified in colonies of monkeys kept for research in 1958 and later detected in humans in 1970. It is a zoonotic viral disease that can spread from animals to humans. It can also spread between people.
Monkeypox Symptoms
- Fever
- Intense headache
- Muscle aches
- Back pain
- Low energy
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Skin rash – this usually begins within 1-3 days of the start of fever.
- Lesions can be flat or slightly raised
In most cases, the symptoms of monkeypox go away on their own within a few weeks, but in some individuals, they can lead to medical complications and even death.
Who is at risk?
- Anyone who has close physical contact with someone who has symptoms of monkeypox
- New-borns
- Children
- People with underlying health conditions
People who were vaccinated against smallpox are likely to have some protection against monkeypox infection.
Tips to protect against monkeypox
- Encourage the infected person to self-isolate, and ask them to cover their lesions by wearing full clothes
- Wear a medical mask while facing them.
- Avoid skin-to-skin contact whenever possible and use disposable gloves if you have any direct contact with lesions.
- Regularly clean your hands with soap and water or an alcohol-based hand rub.
- Wash the person’s clothes, towels, and bedsheets, and eat utensils with warm water and detergent.
Vaccines for monkeypox
There are several vaccines available to prevent smallpox that also provide some protection against monkeypox.
The number of confirmed cases of monkeypox worldwide has reached 219 outside of countries where it is endemic, according to the European Union’s disease agency. We all need to raise awareness about monkeypox among people. It is essential that no one stigmatizes anyone who is affected by this event.
(Disclaimer: The content on this site is for informational purposes only, and should not be taken as professional medical advice. Always seek the guidance of your doctor or other health professionals for any questions you may have regarding your health or a medical condition.)
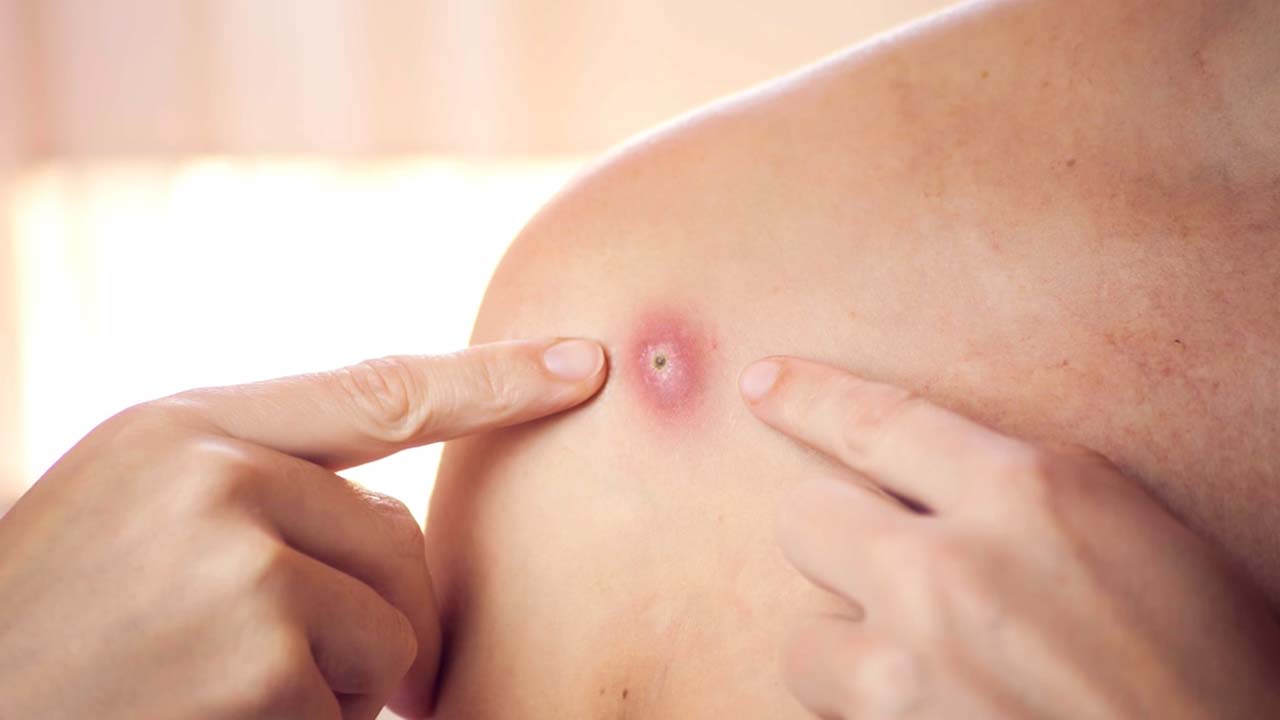
 Monkeypox is a disease caused by the monkeypox virus. It is a zoonotic viral disease that can spread from animals to humans. It can also spread between people.
Monkeypox is a disease caused by the monkeypox virus. It is a zoonotic viral disease that can spread from animals to humans. It can also spread between people.










.jpeg)


.jpg)






.jpeg)



.jpg)


.jpg)




.jpg)


