Scientists from the Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine, under the Moscow Health Department, have conducted a study affirming the efficacy of artificial intelligence services in conducting large-scale breast cancer screenings. The study reveals that neural networks utilized in Moscow's medical system exhibit sensitivity and specificity levels on par with those of an average radiologist.
"Our research demonstrates that AI-based technologies employed for breast cancer screening in Moscow possess sensitivity and specificity comparable to medical professionals. This scientific inquiry was based on the successful application of computer vision technologies in healthcare, a development that promises to significantly reduce doctors' workload and expedite patient outcomes.
Starting in 2023, Moscow has introduced a pioneering health insurance rate within Russia, dedicated to the analysis of breast cancer screening employing AI services. During this period, over 100,000 mammograms have been analyzed by doctors using AI. Breast cancer constitutes a substantial medical, socioeconomic, and demographic challenge, representing the leading oncological pathology and the primary cause of female mortality. In more than 27% of cases, malignant tumors are detected in the later stages. However, the consistent rise in the population accumulation index signals systematic advancements in breast cancer detection and treatment methods, with the indicator increasing from 9.5 in 2011 to 11.9 in 2021. Russia conducts approximately 8.2 million breast cancer screenings annually, necessitating significant time, manpower, and financial resources for double reading. The application of AI services for initial mammogram evaluation offers a solution to reduce these costs while maintaining or enhancing diagnostic quality, as explained by Anton Vladzimirsky, Deputy Director for Scientific Research at the Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine under the Moscow Health Department. Presently, AI aids in the detection of various diseases across more than 20 medical fields, having already processed over 10 million imaging tests. The experiment involves the participation of around 150 medical organizations, 1,500 radiologists, and over 50 AI services. AI technology assists in identifying conditions such as lung cancer, COVID-19, spinal osteoporosis, aortic aneurysms, coronary heart disease, stroke, pulmonary hypertension, hydrothorax, breast cancer, spinal hernias, flat feet, and numerous other disorders in X-ray images. Moscow has embarked on a digitalization journey in healthcare for over a decade, actively embracing AI-based technologies. In 2020, the Moscow City Hall's Social Development Complex, in collaboration with the Department of Information Technology, initiated a pioneering project at the Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine of the Moscow Health Department, pioneering the integration of computer vision into radiology diagnostics.
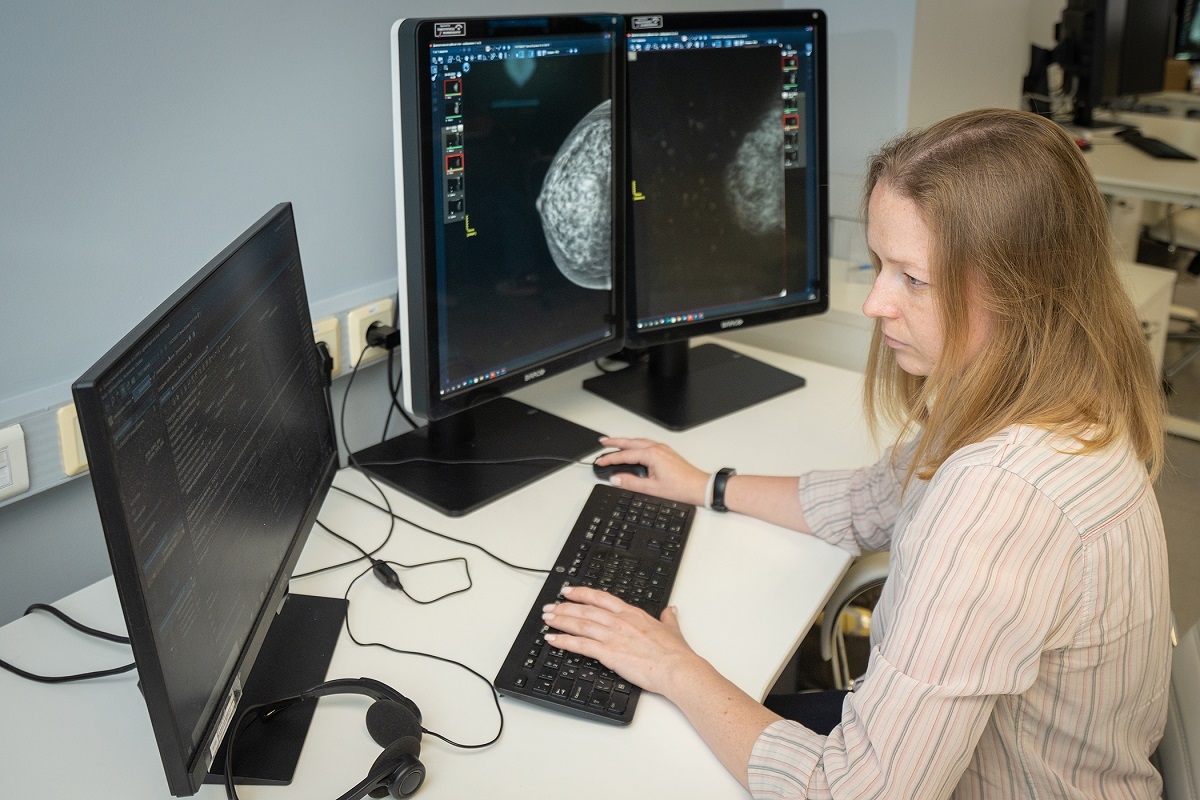
 The integration of neural networks into breast cancer screening has the potential to yield substantial cost savings nationwide and enhance accessibility to preventive screenings," emphasized Yuri Vasilev, Senior Consultant for Radiology and CEO of the Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine.
The integration of neural networks into breast cancer screening has the potential to yield substantial cost savings nationwide and enhance accessibility to preventive screenings," emphasized Yuri Vasilev, Senior Consultant for Radiology and CEO of the Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine.










.jpeg)

.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)

.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
_(1).jpeg)

_(1)_(1)_(1).jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)






