First-born children have a lower risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes than brothers and sisters born later, but people who are part of a large family with many siblings have an increased risk of these events, suggests the results of a large population study in Sweden, published in the online journal BMJ Open.
It is well-known that family history – the health of parents and grandparents – has an impact on a person’s health, including their risk of cardiovascular events, but now there is growing interest in what influence the make-up of a person’s immediate family – the number and age of siblings – might have.
The authors accessed data on 1.36 million men and 1.32 million women born between 1932 and 1960 and aged 30–58 years in 1990 from the Multiple-Generation Register in Sweden. Data on fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular and coronary events over the next 25 years were retrieved from national registers.
Analysis of the data showed that first-borns had a lower risk of non-fatal cardiovascular and coronary events than siblings born later. First-born men had a higher risk of death than second and third-born siblings, while first-born women had a higher risk of death than second-born siblings, but equal to further siblings.
When the family size was looked at, compared with men with no siblings, men with one or two siblings had a lower risk of cardiovascular events, while those with four or more siblings had a higher risk.
Similarly, compared with men with no siblings, men with more than one sibling had a lower risk of death, while those with three or more siblings had an increased risk of coronary events.
A similar pattern was seen in women. Compared with those with no siblings, women with three or more siblings had an increased risk of cardiovascular events, while those with two or more siblings had an increased risk of coronary events. Women with one or more siblings had a lower risk of death.
This is an observational study, and as such, can’t establish cause. The authors also highlight some limitations, including that the Swedish registers included no information on diagnostic procedures and there were no data on lifestyle factors, such as body mass index, smoking, and diet.
However, socioeconomic status, obesity, diabetes, chronic lung disease (COPD) and alcoholism, and related liver disorders were taken into account. They also note that some of their findings conflict with those from previous studies.
The authors point out that, as policies to support families and the number of children currently vary widely between countries, their findings could have implications for public health.
“More research is needed to understand the links between sibling number and rank with health outcomes,” they say. “Future research should be directed to find biological or social mechanisms linking the status of being firstborn to lower risk of cardiovascular disease, as indicated by our observational findings.”
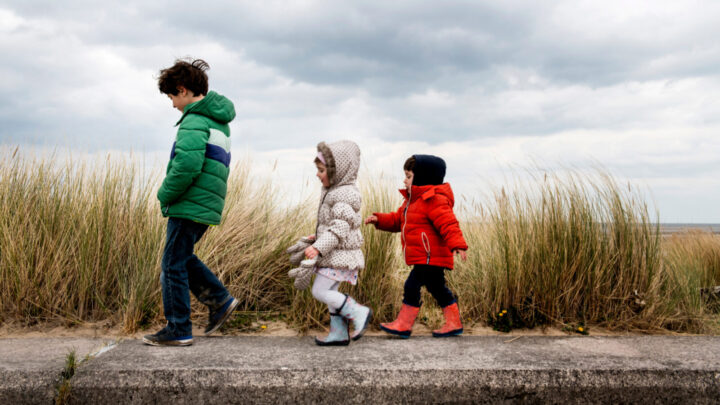

 First-born children have a lower risk of cardiovascular events, but having lots of siblings is associated with an increased risk
First-born children have a lower risk of cardiovascular events, but having lots of siblings is associated with an increased risk

















.jpeg)

.jpeg)










.jpg)




.jpg)

