Headaches are an all-too-familiar condition affecting millions across the globe. The World Health Organization (WHO) reveals that nearly 40% of the world’s population experiences some form of headache, with women being disproportionately affected. These unwelcome episodes can range from mild and fleeting to severe and debilitating, disrupting daily lives and demanding medical attention.
Understanding the types, causes, and treatments of headaches can help demystify this common ailment and offer actionable strategies for relief.
Not all headaches are the same. They vary in duration, intensity, and origin. Broadly, headaches are classified into two main categories:
1. Primary Headaches: These occur independently, without any underlying medical condition. The most prevalent types include:
Migraines: Known for their pulsating or throbbing pain, migraines often follow a predictable pattern and are more common in younger individuals. They may be accompanied by an “aura,” which includes sensory disturbances such as flashing lights, blind spots, or tingling sensations. Migraines can also cause nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and even temporary difficulty speaking.
Tension-Type Headaches: Characterized by a dull, aching sensation, tension headaches are typically caused by stress, fatigue, or muscle strain. Unlike migraines, they don’t usually come with additional neurological symptoms.
2. Secondary Headaches: These are symptoms of an underlying condition. Causes can range from trauma and sinus infections to structural brain lesions or psychiatric disorders. Secondary headaches often signal a need for medical evaluation, especially if accompanied by unusual symptoms like fever, neck stiffness, or balance issues.
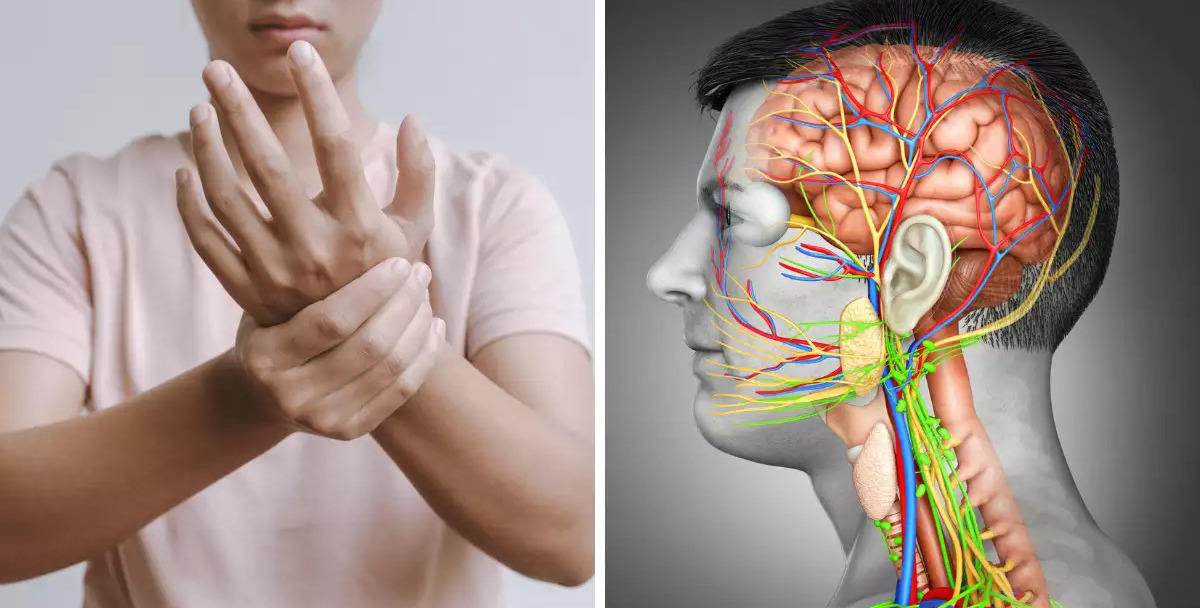
Migraines stand out as one of the most disruptive forms of headaches. They affect a significant portion of the population, particularly women. Migraine episodes often follow a consistent history or pattern, making them somewhat predictable for those who experience them.
One hallmark of migraines is the aura phase, which sets them apart from other headache types. Common aura symptoms include:
Visual disturbances: Flashing lights, zigzag patterns, or temporary blind spots.
Sensory changes: Tingling or numbness, often on one side of the body.
Speech difficulties: Slurred speech or confusion.
These symptoms can occur before or during the headache phase, adding to the complexity of migraines. While not every migraine includes an aura, recognizing these signs is crucial for timely intervention.
While most headaches are harmless, certain red flags should never be ignored. A sudden change in headache patterns or the appearance of new symptoms could indicate an underlying issue that requires immediate attention.
Warning signs include:
Persistent or worsening headaches over time.
Headaches triggered by physical activity or coughing.
Accompanying symptoms such as fever, neck stiffness, confusion, or decreased consciousness.
Headaches stemming from disorders of the neck, eyes, teeth, or facial structures often require targeted treatment, as they involve specific regional causes.
Effective headache management begins with accurate diagnosis. Once the type and cause of a headache are identified, tailored treatments can provide relief.
1. Over-the-Counter Solutions: For many, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or aspirin are the first line of defence against acute pain. These medications reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and bring down fever.
2. Prescription Medications: In cases of migraines, doctors often prescribe a combination of:
Antiemetics: These drugs address nausea and vomiting associated with severe headaches.
Triptans and Ergotamines: These are migraine-specific medications that work by targeting serotonin receptors to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation in the brain.
Treatment plans are tailored based on individual factors such as body weight, medical history, and overall health.
3. Lifestyle Adjustments: For chronic sufferers, lifestyle changes can make a significant difference. These include:
Stress management: Techniques like mindfulness, yoga, and deep breathing can reduce the frequency of tension headaches.
Regular exercise: Physical activity improves circulation and reduces stress, helping prevent headaches.
Dietary considerations: Avoiding trigger foods like caffeine, alcohol, or processed snacks can minimize migraine occurrences.
Preventing headaches often involves understanding personal triggers. Keeping a headache diary can help identify patterns, such as specific foods, stress levels, or sleep habits that precede episodes. Once triggers are recognized, avoiding them becomes easier.
For migraines, preventive medications may be prescribed to reduce the frequency and severity of attacks. These include beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and certain antidepressants.
In recent years, alternative therapies have gained traction for headache relief. While not a replacement for medical treatments, these methods can complement traditional approaches:
Acupuncture: Inserting fine needles into specific points on the body to alleviate tension and pain.
Massage therapy: Targeting tension in the neck, shoulders, and back to reduce stress-induced headaches.
Essential oils: Aromatherapy using peppermint or lavender oils may provide soothing effects during a headache.
Research shows that women are more likely to experience headaches than men, particularly migraines. Hormonal fluctuations play a significant role, with many women reporting headaches around their menstrual cycle or during pregnancy.
Understanding this link has led to the development of targeted treatments, including hormonal therapies for migraine prevention. Additionally, lifestyle modifications tailored to hormonal changes can help manage symptoms more effectively.
Ignoring frequent headaches can lead to a decline in quality of life, affecting productivity, relationships, and mental health. Chronic headaches are also linked to conditions like anxiety and depression, creating a cycle that can be challenging to break.
Seeking medical advice early ensures that underlying causes are identified and treated promptly. With the right combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and preventive strategies, most people can manage their headaches effectively and lead healthier lives.
Headaches may be common, but they are far from simple. Understanding the different types, recognizing warning signs, and exploring tailored treatment options can help individuals regain control over their lives.
Whether it’s a throbbing migraine, a stress-induced tension headache, or a secondary headache signalling a deeper issue, there’s hope for relief through medical advancements and lifestyle changes. By prioritizing prevention and seeking timely care, headaches no longer have to dictate the rhythm of daily life
http://www.21stcenturyhospitalgownplus.com/
http://www.elite-factory-15.fr/
http://www.gba-amateurboxen.de/
http://www.kita-strausberg.de/
http://sonispicehelensburgh.co.uk/
http://curryzonecardonald.co.uk/
http://cinnamon-edinburgh.co.uk/
http://www.bombaydelipaisley.com/
http://pizzanightclydebank.co.uk/
http://www.pizzanightclydebank.com/
http://gyros2goclydebank.co.uk/
http://grillicious-glasgow.co.uk/
http://www.abdulstakeaway.com/
http://www.freddiesfoodclub.com/
http://cinnamonportobello.co.uk/
http://www.romafishnchips.com/
http://bombaydelipaisley.co.uk/
http://yaraloungerestaurant.co.uk/
http://tasteofchinacoatbridge.co.uk/
http://www.memoriesofindiagorebridge.com/
http://memoriesofindiaeh23.co.uk/
http://freddiesknightswood.co.uk/
http://gyros2gohardgate.co.uk/
http://www.strausseeschwimmen.de/
http://www.janstanislawwojciechowski.pl/
http://london-takeaways.co.uk/
http://shahimanziledinburgh.co.uk/
http://freddiesfoodclub.co.uk/
http://www.spicestakeaway.com/
http://www.mexita-paisley.com/
http://pandahouseglasgow.co.uk/
http://www.zum-alten-steuerhaus.de/
http://www.oberstufenzentrum-mol.org/
http://www.morsteins-neuenhagen.de/
http://www.maerkische-jugendweihe.de/
http://www.planungsbuero-henschel.de/
http://www.hertzelektronik.de/
http://www.militaergefaengnisschwedt.de/
http://www.fahrrad-naumann.de/
http://www.hondamoto-villemomble.com/
http://www.hondamoto-royan.com/
http://www.hondamoto-ajaccio.com/
http://www.download-skycs.com/
http://www.sisakoskameleon.hu/
http://www.hondamoto-montauban.com/
http://www.hondamoto-chalonsursaone.com/
http://www.hondamoto-champignysurmarne.com/
http://www.hondamoto-asnieres.com/
http://www.pasquier-motos.com/
http://www.evacollegeofayurved.com/
http://www.compro-oro-italia.it/
http://www.hondamoto-saintmaximin.com/
http://www.hoangminhceramics.com/
http://www.pasiekaambrozja.pl/
http://www.xn--b1alildct.xn--p1ai/
http://www.ferreteriaflorencia.com/
http://www.thevichotelkisumu.com/
http://www.nexuscollection.com/
http://www.moitruongminhhuy.com/
http://www.ozkayalarpaslanmaz.com/
http://www.munkagepmonitor.hu/
http://www.my247webhosting.com/
http://www.thesmokingribs.com/
http://www.healthlabgrosseto.it/
http://www.ochranakaroserie.cz/
http://www.phukiendonginox.com/
http://www.meijersautomotive.nl/
http://www.kartaestudentit.al/
http://www.podlahyjihlavsko.cz/
http://www.hillhouseequestrian.com/
http://www.gradskapivnicacitadela.com/
http://www.capella-amadeus.de/
http://www.landfleischerei-auris.de/
http://www.faistesvacances.be/
http://www.autoservice-doernbrack.de/
http://www.tabakhaus-durek.de/
http://www.oldtimer-strausberg.de/
http://www.imexsocarauctions.com/
http://www.kaslikworkshop.com/
http://www.firefightercpr.com/
http://www.visuallearningsys.com/
http://www.hanksautowreckers.com/
http://www.impresospichardo.com/
http://www.philiphydraulics.net/
http://www.internationaldentalimplantassociation.com/
http://www.indywoodtalenthunt.com/
http://www.badicecreamgame.com/
http://www.riad-amarrakech.com/
http://www.centrodeformacioncanario.com/
http://www.socialdefender.com/
http://www.pepiniere-paravegetal.com/
http://www.reparertelephonearles.fr/
http://www.namsontrongdoi.com/
http://www.devipujakjivansathiseva.in/
http://www.laymissionhelpers.org/
http://www.vangiaphatdeco.com/
http://www.isscoachinglucknow.in/
http://www.hieuchuandoluong.com/
http://www.aurorabienesraices.com/
http://www.indianmoversassociation.com/
http://www.oztopraklarotomotiv.com/
http://moitruongnamnhat.com.vn/
http://www.dienmayvinhthuan.vn/
http://www.divadelkoproskoly.cz/
http://www.xn--12cfje1df4hdl7f1bf2evg9e.com/
http://www.westernirontrailers.com/
http://www.jazzaufildeloise.fr/
http://www.signcraft-drone.com/
http://www.realtyhighvision.com/
http://www.thermexscandinavia.nl/
http://imobiliariafelipe.com.br/
http://www.salon-lindenoase.de/
http://www.jezirka-zahrada.cz/
http://www.singhanialogistics.in/
http://www.der-pixelmischer.de/
http://www.hegermuehlen-grundschule.de/
http://www.radiologie-strausberg.de/
http://www.foto-studio-matte.de/
http://www.tables-multiplication.com/
http://www.rusztowania-belchatow.pl/
http://www.fishingandhuntingheaven.com/
http://www.orologiegioiellilameridiana.it/
http://www.rotarybresciaest.org/
http://www.jacarandaspain.com/
http://www.javieririberri.com/
http://www.huebelschraenzer.ch/
http://www.illinoiscreditunionjobs.com/
http://www.iznikdenizorganizasyon.com/
http://www.leasebackconcierge.com/
http://www.eoisantacoloma.org/
http://skullbasesurgery.co.uk/
http://www.immobilienplattensee.com/
http://www.germandailynews.com/
http://www.gptdcinternational.com/
http://www.forklifttrainingedmonton.com/
http://www.kashiwanakayama-cl.com/
http://www.thehousemediagroup.com/
http://www.pensiimaramures.ro/
http://www.michaelakokesova.cz/
http://www.viswabrahmanaeducationaltrust.com/
http://krone-aluminium.com.pl/
http://www.broadwaylumber.com/
http://www.ambulancesoccasions.com/
http://www.continuumintegrated.com/
http://www.joilifemarketing.com/
http://www.rotaseydisehir.com/
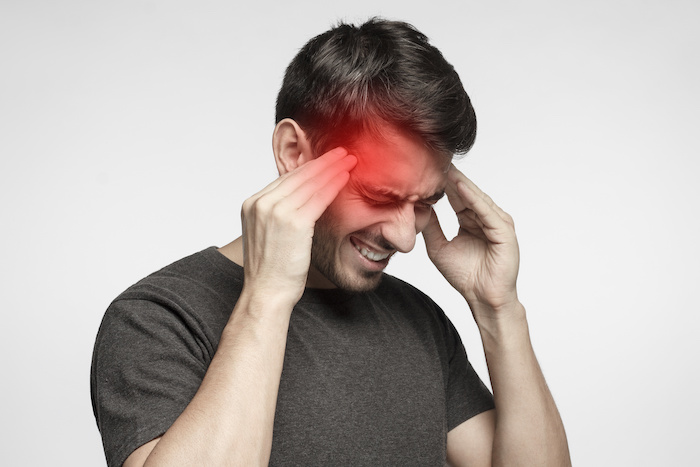

 By prioritizing prevention and seeking timely care, headaches no longer have to dictate the rhythm of daily life.
By prioritizing prevention and seeking timely care, headaches no longer have to dictate the rhythm of daily life.
















.jpeg)

.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)

.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
_(1).jpeg)

_(1)_(1)_(1).jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)






