Irregular growth of the thyroid gland is termed goiter. The most common cause of goiter is Iodine deficiency. Improper regulation of thyroid hormone or over enlargement of the thyroid is associated with goiter.
Functions of thyroid hormone
- Regulation of the conversion of food into energy (metabolism)
- Regulation of body temperature
- Regulation of heart rate
- Regulation of blood pressure
- Regulation of other hormone interactions
- Regulation of growth during childhood
Most people having goiter have no signs and symptoms except swelling at the base of the neck.
Signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism (lower production of thyroid hormone)
- Fatigue
- Increased sensitivity to cold
- Increased sleepiness
- Dry skin
- Constipation
- Muscle weakness
- Problems with memory or concentration
Signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism (increased production of thyroid hormone)
- Weight loss
- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
- Increased sensitivity to heat
- Excess sweating
- Tremors
- Irritability and nervousness
- Muscle weakness
- Frequent bowel movements
- Changes in menstrual patterns
- Sleep difficulty
- High blood pressure
- Increased appetite
Hyperthyroidism in children can cause rapid growth in height and changes in behavioral patterns.
The increasing size and shape of the goiter obstruct the airway or voice box. The symptoms include
- Difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty breathing with exertion
- Cough
- Hoarseness
- Snoring
Goiter causes
Deficiency of iodine - Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones. If a person does not get enough dietary iodine, hormone production drops and the pituitary gland signals the thyroid to make more. This increased signal results in excess thyroid growth.
Hashimoto’s disease - Hashimoto's disease is an autoimmune disorder, an illness caused by the immune system attacking healthy tissues. The damaged and inflamed tissues of the thyroid don't produce enough hormones (hypothyroidism).
Thyroid nodules - A nodule is the irregular growth of thyroid cells that form a lump. A person may have one nodule or several nodules. The cause of nodules is not clear, but there may be multiple factors — genetics, diet, lifestyle, and environment. Most thyroid nodules are noncancerous (benign).
Thyroid cancer - Thyroid cancer is a less common cancer and is generally treatable. About 5% of people with thyroid nodules are found to have cancer.
Pregnancy - Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) hormone produced during pregnancy, may cause the thyroid gland to be overactive and enlarge slightly.
Inflammation - Thyroiditis is inflammation of the thyroid caused by an autoimmune disorder, bacterial or viral infection, or medication.
Risk factors of goiter
- Deficiency of dietary Iodine - Iodine is found primarily in seawater and in the soil in coastal areas. People who are lacking Iodine in their diet or supplements that contain Iodine are at increased risk.
- Being female – Thyroid hormone disorders are more prevalent in females.
- Pregnancy and menopause – Pregnancy and menopause increase the risk of contracting thyroid-related disorders.
- Age – They are more common after the age of 40.
- Medicine – Certain medicines increase the risk.
- Family medical history – A family history of goiter or thyroid abnormalities or genetic factors are the risk factors for this.
- Radiation exposure – Exposure to radiation to your neck or chest area increases the risk.
(Disclaimer: The content on this site is for informational purposes only, and should not be taken as professional medical advice. Always seek the guidance of your doctor or other health professionals for any questions you may have regarding your health or a medical condition.)
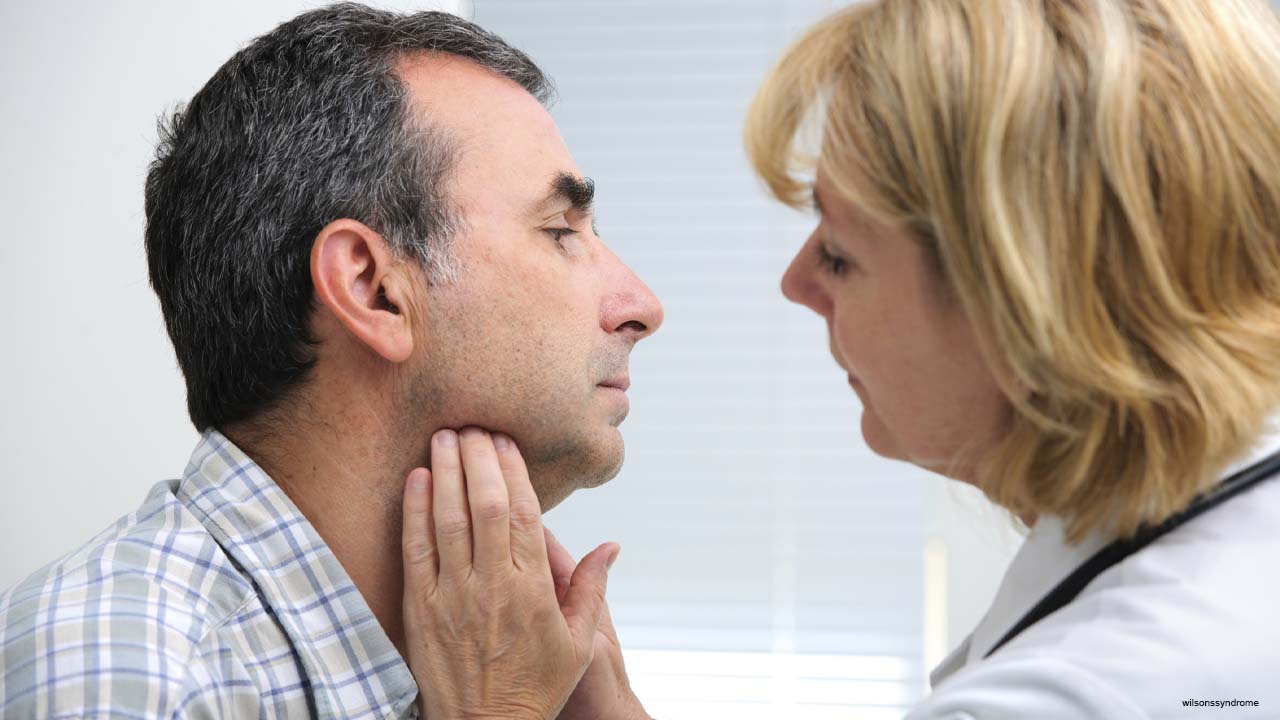
 Living an unhealthy lifestyle is giving rise to several autoimmune disorders. Improper functioning of the thyroid gland is also an autoimmune disease. This includes hypo, hyper, thyroiditis, goiter, and many others. The main cause of goiter is Iodine deficiency. Let’s look at the symptoms and risk factors.
Living an unhealthy lifestyle is giving rise to several autoimmune disorders. Improper functioning of the thyroid gland is also an autoimmune disease. This includes hypo, hyper, thyroiditis, goiter, and many others. The main cause of goiter is Iodine deficiency. Let’s look at the symptoms and risk factors.










.jpeg)

.jpg)






.jpeg)



.jpg)


.jpg)




.jpg)


