KNOW Bio, LLC has generated the first definitive evidence that nitric oxide (NO) can inhibit viral reproduction of SARS-CoV-2, the human coronavirus that causes COVID-19. Nitric oxide is a molecule produced naturally by the body to regulate blood flow, control inflammation, and defend against invading microorganisms.
These milestone in-vitro experiments were conducted by testing multiple nitric oxide-releasing compounds against wild type SARS-CoV-2 virus at an independent laboratory with a deep history of antiviral research. Therapeutic doses (<200 µM) were applied to infected VERO E6 cells and showed a dose-dependent effect on viral replication. The result was a greater than 99.9% reduction in virus observed after 24 hours versus virus observed on untreated cells. Furthermore, there was no cytotoxic impact (cell damage or cell death) on uninfected cells.
"We are the first to confirm the potent biological activity of nitric oxide against SARS-CoV-2, the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19," said Neal Hunter, Chief Executive Officer, KNOW Bio, LLC. "As a leader in the development of NO-based therapies, we felt we were best positioned to establish that NO is effective against this virus."
Previous reports have only speculated on the potential of nitric oxide to serve as a therapeutic for patients with COVID-19 or as a preventative countermeasure for those who are at risk of exposure to the virus.1 These conjectures were based in large part on prior published scientific evidence derived from studies conducted on the original SARS-CoV virus.
"The expansive literature supporting nitric oxide's function as a broad-spectrum antimicrobial, shows that nitric oxide-based approaches can play a role in preventing, limiting, and/or treating the pulmonary consequences of COVID-19," said Mark Schoenfisch, Ph.D., Chief Scientific Officer, KNOW Bio, LLC.
Nitric Oxide (NO) has been reported to:
Inhibit coronavirus infection by altering spike protein binding and disrupting the ability of the virus to attach to the receptor and infect human cells.2
Inhibit coronavirus viral replication inside an infected cell by slowing viral RNA production - resulting in fewer RNA strands and viral copies.3
Inhibit release of reproduced virus by preventing host cell death via interfering with caspase activity - the reproduced virus particles thus remain within the infected cell and fewer virus particles are spread to infect other cells.4
"We have gained new understandings into the effective concentrations, rates of release and mechanism of action of nitric oxide against human coronavirus - providing valuable insights into safety and efficacy," continued Schoenfisch.
Submission for publication and peer review is expected before year end.
"There are millions of lives being disrupted and hundreds of thousands lost to this frightening virus," Hunter continued. "Our findings clearly show that nitric oxide-based therapeutics must be a part of any well-thought response to the COVID-19 pandemic."
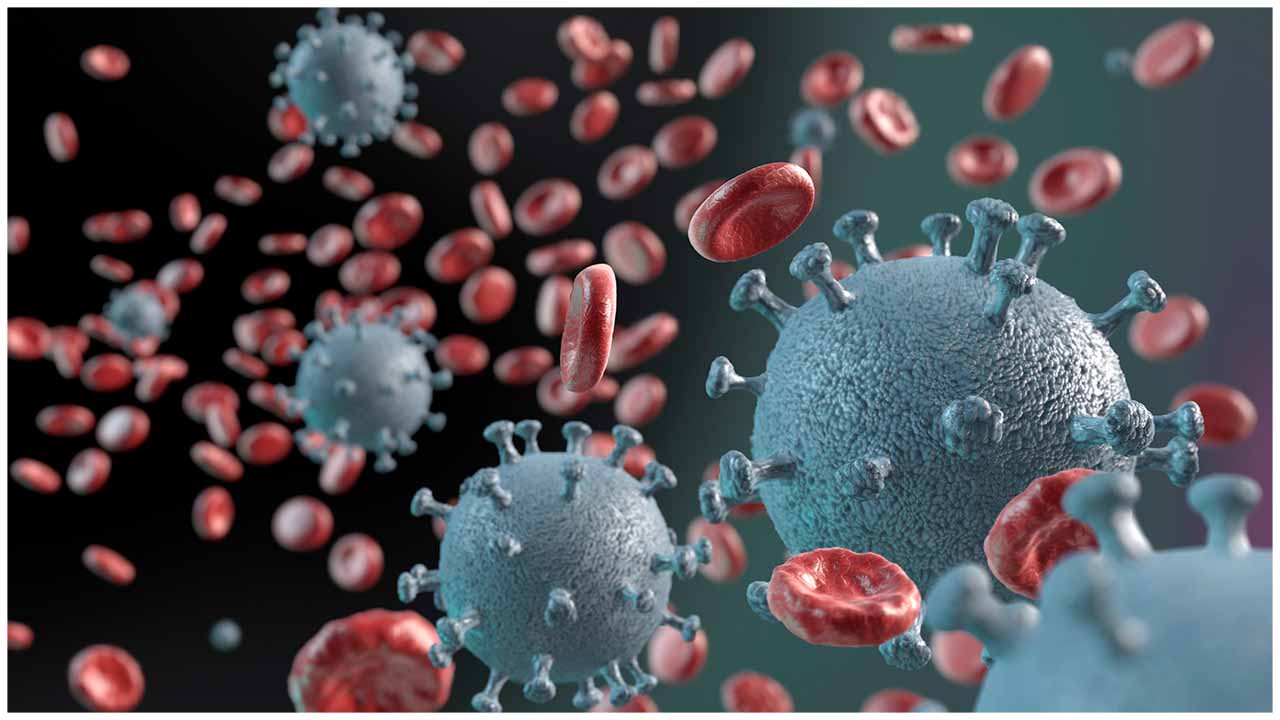
 Nitric oxide is a molecule produced naturally by the body to regulate blood flow, control inflammation, and defend against invading microorganisms.
Nitric oxide is a molecule produced naturally by the body to regulate blood flow, control inflammation, and defend against invading microorganisms.







.png)
.jpg)
.png)







.jpeg)








.jpg)




.jpg)




