Lymphoma is a malignant growth of the lymphatic system. It develops in lymphocytes, which are a sort of white blood cells. These cells help battle diseases in the body and assume a fundamental part in the body's immune defenses.
As this kind of malignancy is available in the lymph system, it can rapidly metastasize, or spread, to various tissues and organs all through the body. Lymphoma frequently spreads to the liver, bone marrow, or lungs.
Individuals of all ages can develop lymphoma, yet it is among the most well-known reasons for a malignant growth in kids and youthful grown-ups matured 15–24 years. It is frequently treatable.
Types of Lymphomas
There are two principal kinds of lymphoma: Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Within these, there are numerous subtypes.
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is the most well-known sort, regularly creates from B and T lymphocytes (cells) in the lymph nodes or tissues all through the body. Tumor development in non-Hodgkin lymphoma may not influence each lymph node, regularly skirting a few and developing on others. Swollen organs that don't disappear can be an indication of lymphoma. It represents 95% of lymphoma cases.
As indicated by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), non-Hodgkin lymphoma represents 4.2% of all tumors in the United States, and an individual's lifetime danger of creating it is about 2.2%.
- Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma is a malignancy of the immune system, and specialists can distinguish it by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, which are unusually huge B lymphocytes. In individuals with Hodgkin lymphoma, the malignancy typically moves from one lymph node to a nearby one.
The NCI gauge that Hodgkin lymphoma represents 0.5% of everything being equal and around 0.2% of individuals in the U.S. will get an analysis in the course of their life.
Symptoms of Lymphomas
The indications of lymphoma are like those of some popular infections, for example, the normal virus. In any case, they regularly proceed for a more broadened period.
A few people won't experience any indications. Others may see a growth of the lymph nodes. There are lymph nodes all around the body. Expanding frequently happens in the neck, crotch, mid-region, or armpits.
The swellings are regularly effortless. They may get excruciating if the amplified organs press on organs, bones, and different structures. A few people mistake lymphoma for back agony.
Lymph nodes can likewise grow during regular contaminations, for example, a virus. In lymphoma, the growth doesn't resolve. Pain is likewise bound to go with the expanding in the event that it has happened because of a disease.
The cover of side effects can prompt misdiagnosis. Any individual who has relentlessly swollen organs should see their PCP for a check-up.
Different side effects of the two kinds of lymphoma may include:
- Continuous fever without disease
- Night sweats, fever, and chills
- Weight reduction and decreased craving
- Irregular tingling
- Persevering exhaustion or absence of energy
- Pain in lymph nodes in the wake of drinking liquor
Some extra side effects of non-Hodgkin lymphoma include:
- Persistent coughing
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling or pain in the stomach
- Pain, shortcoming, loss of motion, or modified sensation may happen if an augmented lymph node presses against spinal nerves or the spinal string.
Lymphoma can spread quickly from the lymph nodes to different pieces of the body through the lymphatic system. As malignant lymphocytes spread into different tissues, the immune system can't shield against contaminations as viably.
Treatment of Lymphomas
Chemotherapy is one of the potential medicines that specialists may use to treat lymphoma. The course of treatment relies upon the kind of lymphoma an individual has and the stage it has reached.
- Slow or moderate developing lymphoma may not require treatment.
- Attentive holding up might be sufficient to ensure the malignant growth doesn't spread.
On the off chance that treatment is important, it might include the accompanying:
- Biologic treatment: This is a medication therapy that animates the safe system to assault the malignancy. The medication accomplishes this by bringing living microorganisms into the body.
- Neutralizer treatment: A clinical expert supplements engineered antibodies into the circulation system. These react to the malignancy's poisons.
- Chemotherapy: A medical care group directs forceful medication therapy to target and execute malignant growth cells.
- Radio-immunotherapy: This conveys powerful radioactive dosages legitimately into harmful B cells and T-cells to wreck them.
- Radiation treatment: A specialist may prescribe this sort of treatment to target and wreck little regions of malignant growth. Radiation treatment utilizes concentrated portions of radiation to murder malignant cells.
- Stem cell transplantation: This can help reestablish harmed bone marrow following high portion chemotherapy or radiation treatment.
- Steroids: A specialist may infuse steroids to treat lymphoma.
- Medical procedure: A specialist may remove the spleen or a different organ after the lymphoma has spread. Nonetheless, a malignancy expert, or oncologist, will all the more usually demand medical procedure to get a biopsy.
Risk factors for Lymphomas
Risk factors for non-Hodgkin lymphoma include:
- Age: Most lymphomas happen in individuals matured 60 years and more seasoned. In any case, a few sorts are bound to create in youngsters and youthful grown-ups.
- Sex: Some sorts are almost certain in ladies. Men have a higher danger of different kinds.
- Identity and area: In the U.S., African American and Asian American individuals have a lower hazard for non-Hodgkin lymphoma than white individuals. Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma is more normal in created countries.
- Synthetic concoctions and radiation: Nuclear radiation and certain rural synthetic substances have connections to non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Immunodeficiency: An individual with a less dynamic safe system has a higher danger. This might be because of hostile to dismissal meds following an organ relocates or HIV.
- Immune system maladies: This sort of ailment happens when the resistant system assaults the body's own cells. Models incorporate rheumatoid joint inflammation and celiac sickness.
- Disease: Certain viral and bacterial contaminations that change lymphocytes, for example, the Epstein-Barr infection (EBV), increment the danger. This infection causes glandular fever.
- Breast implants: These can prompt anaplastic enormous cell lymphoma in the bosom tissue.
- Bodyweight and diet: The American Cancer Society (ACS) has proposed that overweight and stoutness may have some inclusion in the improvement of lymphoma. Nonetheless, more examination is important to affirm the connection.
Hodgkin lymphoma
Risk factors for Hodgkin lymphoma include:
- Irresistible mononucleosis: The Epstein-Barr infection (EBV) can cause mononucleosis. This infection expands the danger of lymphoma.
- Age: People matured 20–30 years and those 55 years old have a higher danger of lymphoma.
- Sex: Hodgkin lymphoma is somewhat more normal in guys than females.
- Family ancestry: If a kin has Hodgkin lymphoma, the danger is somewhat higher. In the event that the kin is an indistinguishable twin, this danger increments essentially.
- HIV contamination: This can debilitate the invulnerable system and increment the danger of lymphoma.
Diagnosis of Lymphomas
A specialist may demand imaging outputs to help analyze lymphoma. There are no normal screenings for lymphoma. On the off chance that an individual has industrious viral side effects, they should look for a clinical check-up.
The specialist will get some information about the individuals and family's clinical history and attempt to preclude different conditions.
They will likewise do a physical assessment, including an examination of the midsection and jawline, neck, crotch, and armpits, where swellings may happen. The specialist will search for indications of disease close to lymph nodes since this can represent most instances of expanding.
Tests for lymphoma
Tests will affirm whether the lymphoma is available.
- Blood tests and biopsies
These can identify the presence of lymphoma and help a specialist recognize various sorts. A biopsy includes a specialist taking an example of lymph tissue. The specialist will at that point send it for assessment in a research center. The specialist may eliminate a little segment or the entirety of a lymph node. Now and again, they may utilize a needle to take a tissue test. It may be important to do a bone marrow biopsy. This may require a neighborhood sedative, a narcotic, or an overall sedative. Biopsies and different tests can affirm the phase of the malignant growth to see whether it has spread to different pieces of the body.
- Imaging tests
A specialist may demand imaging filters, for example, a CT scan, an MRI scan, a PET scan, X-beam imaging of the chest, stomach, and pelvis
- Ultrasound
Ultrasound may be used to look for enlarged lymph nodes throughout the body and determine whether the lymphoma has spread.
- A spinal tap
In this technique, a specialist utilizes a long, flimsy needle to eliminate and test spinal liquid under the neighborhood sedative.
Staging of the disease relies upon the sort, development rate, and cell attributes. In stage 0 or 1, the malignant growth remains in a limited territory. By stage 4, it has spread to more far off organs, and specialists think that it’s additionally testing to treat.
A specialist may likewise portray lymphoma as indolent, implying that it stays in a single spot. A few lymphomas are forceful, which implies they spread to different pieces of the body.
With treatment, over 72% of individuals with an analysis of non-Hodgkin lymphoma will make due for in any event 5 years.
With Hodgkin lymphoma, 86.6% of individuals who get treatment will get by for in any event 5 years.
The odds of a decent result decline as lymphoma advances. It is fundamental to look for clinical consideration for any manifestations of cold or contamination that proceeds for an all-inclusive period. Early determination can improve an individual's odds of effective treatment.
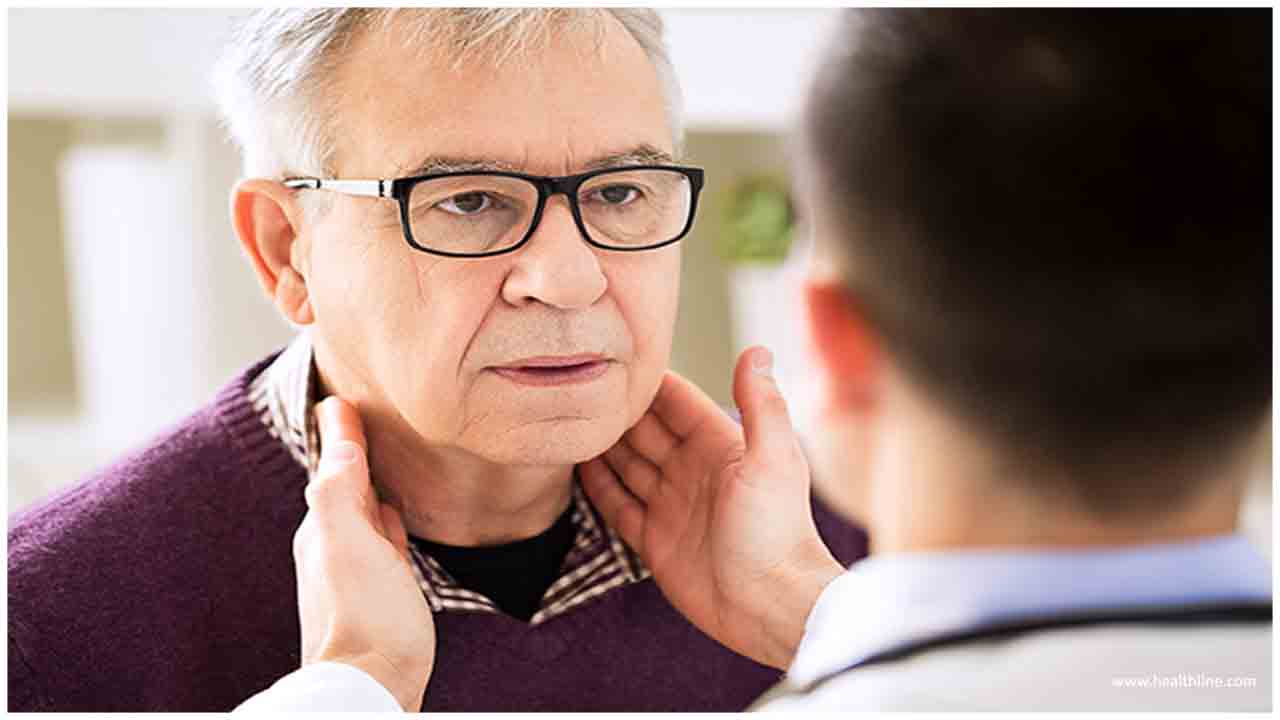
 A few people won't experience any indications. Others may see a growth of the lymph nodes. There are lymph nodes all around the body. Expanding frequently happens in the neck, crotch, mid-region, or armpits.
A few people won't experience any indications. Others may see a growth of the lymph nodes. There are lymph nodes all around the body. Expanding frequently happens in the neck, crotch, mid-region, or armpits.









.jpeg)


.jpg)





.jpeg)



.jpg)


.jpg)




.jpg)


