Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that grow in or on the uterus. Fibroids may grow in the uterine cavity within the wall of the uterus, or outside the uterus, and they can cause painful symptoms. However, half of the uterine fibroids are asymptomatic.
Symptoms
Pelvic pressure or pain
Backache or leg pain
Constipation
Heavy menstrual bleeding
Frequent urination
Pain during intercourse
Urinary retention, or being unable to empty the bladder completely
Risk factors
Family history – If there is a family history of fibroids, this makes your risk three times higher than average.
Diet – Vitamin D deficiency, consuming a red meat-rich diet, and drinking alcohol are associated with increased risk of fibroids.
Weight - Being overweight or obese increases your risk of developing uterine fibroids.
Age – Females of menstruating age group are at higher risk for fibroids. Reproductive hormones promote the growth of fibroids. Uterine fibroids don’t usually develop before puberty or after menopause.
Diagnosis
Uterine fibroids are usually diagnosed by ultrasound. Moreover, MRI and CT scans can also be used to determine the number, size, and location of any fibroids.
Treatment
Shrinking the size of fibroids with medicines - Medications like gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists can suppress the production of estrogen and progesterone, decreasing the size of uterine fibroids.
Shrinking the size of fibroids with a medical procedure – A minimally invasive procedure called uterine artery embolization blocks blood flow to the uterus temporarily, which can shrink fibroids and cause them to die.
Treating fibroids with myomectomy - Procedures like MRI-guided focused ultrasound surgery, myomectomy, or radiofrequency ablation destroy or remove fibroids without affecting uterine tissue.
Removal of the uterus - Hysterectomy, the surgical removal of the uterus is the permanent way to treat fibroids.
Disclaimer: The content on this site is for informational purposes only, and should not be taken as professional medical advice. Always seek the guidance of your doctor or other health professionals for any questions you may have regarding your health or a medical condition.
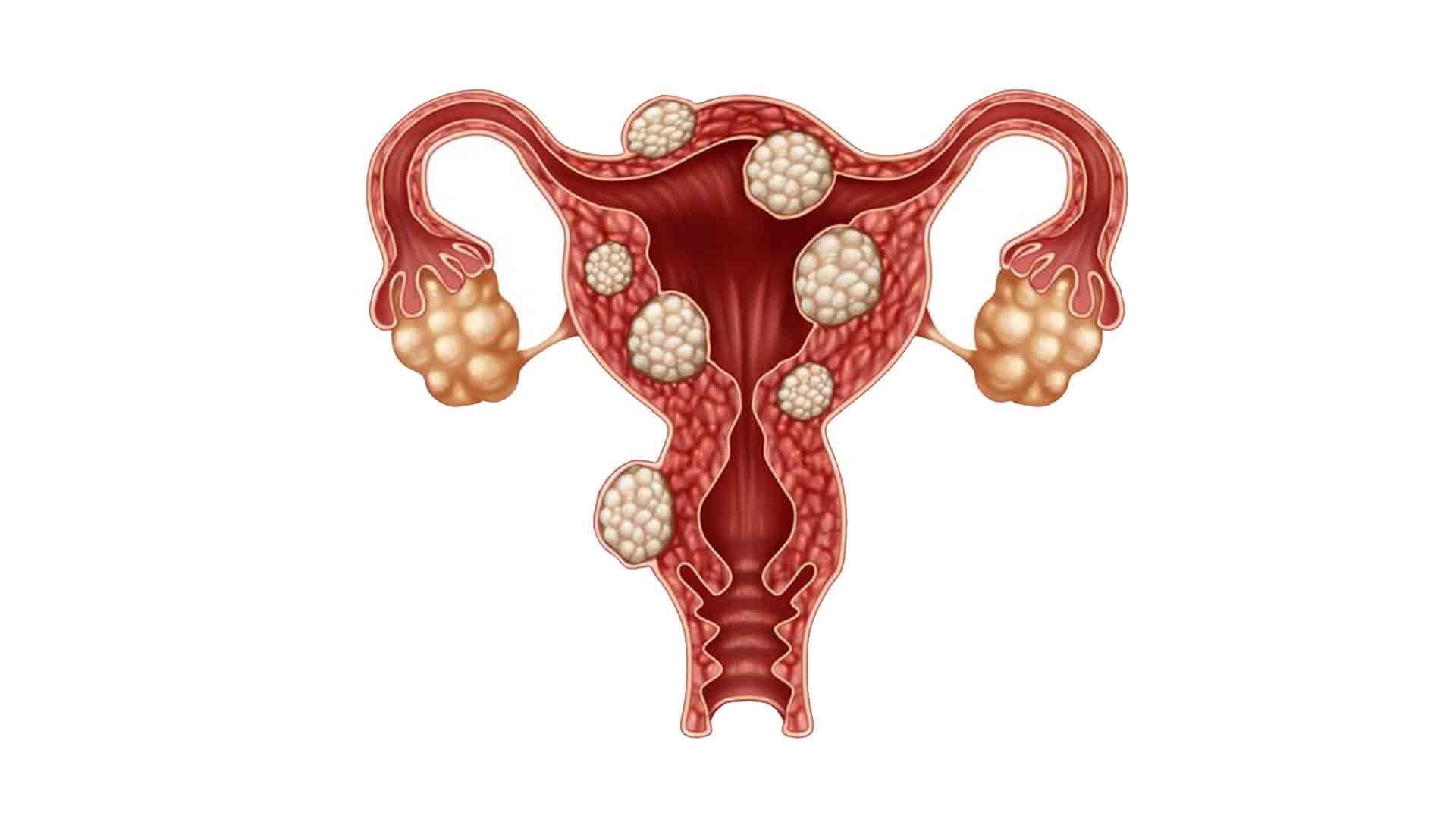
 Uterine fibroids can be asymptomatic. Weight, age, and family history are some of the risk factors for fibroids. They are diagnosed mostly by ultrasound and treated with laparoscopy and hysteroscopy.
Uterine fibroids can be asymptomatic. Weight, age, and family history are some of the risk factors for fibroids. They are diagnosed mostly by ultrasound and treated with laparoscopy and hysteroscopy. 



















.jpeg)


.jpeg)



.jpeg)
.jpeg)






.jpeg)





