Syphilis is a Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) caused by a bacterial infection called Treponema pallidum. The infection gets transmitted through sexual contact with an infected person. It spreads from person to person through direct contact with a syphilis sore (ulcer). These sores are present in the vagina, anus, rectum, lips, and in mouth. It also can pass through broken skin on other parts of the body. Generally, the sores are painless but if it’s not early diagnosed or treated on time or left untreated, the infection can affect other organs in the body such as the heart and brain. Hence early diagnosis is important.
Signs and symptoms
Syphilis doesn’t show any symptoms for years; hence person may not realize and remain at risk for late complications. Signs and symptoms may vary depending upon different stages.
Primary stage – Painless, firm, small and single sore
Secondary stage – Appearance of rash, fever, swollen lymph glands, sore throat, patchy hair loss, headaches, weight loss, muscle aches and fatigue.
Latent stage – The disease may damage vital organs of the body like brain, nerves, eyes etc.
Complications
Syphilis can put you at risk of HIV infection because of the existence of open sores. If you are pregnant, syphilis can affect the baby in your womb. There is also a higher chance of premature birth.
It can cause heart problems and nerve problems such as stroke, meningitis, visual problems, dementia.
Diagnosis
Swab tests and blood tests are the ways to diagnose a person infected with syphilis.
Treatment
Effective treatment of syphilis is available which can prevent severe complications. Syphilis screening is done. The treatment of infection becomes easy if it is early diagnosed. It is treated with penicillin given intramuscularly.
Prevention
1. The best way to prevent an STI is to abstain from having sex. The transmission of syphilis cannot be prevented by washing the genitals, urinating, and/or douching after sex.
2. If you develop any unusual discharge, sores, or rashes, particularly on your genitals, refrain from sex and see your doctor immediately for treatment.
3. It is important that sex partners talk openly if they have sexually transmitted infections to stop/prevent the spread of disease.
Disclaimer: The content on this site is for informational purposes only, and should not be taken as professional medical advice. Always seek the guidance of your doctor or other health professionals for any questions you may have regarding your health or a medical condition.
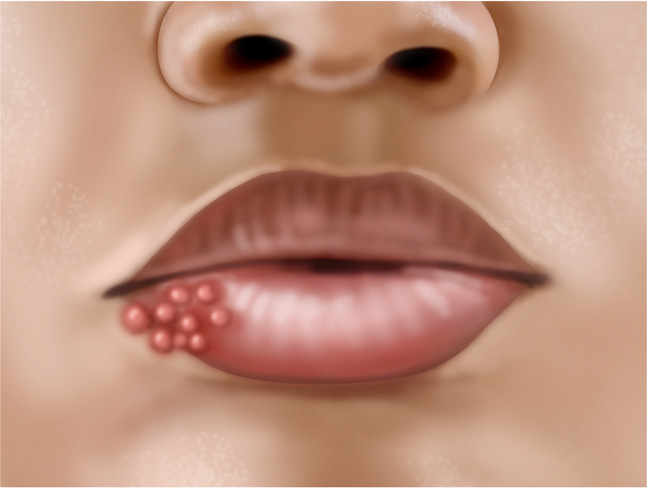
 Know everything about Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) – Syphilis, its causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention
Know everything about Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) – Syphilis, its causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention







.jpg)










.jpeg)



.jpg)







.jpeg)

.jpg)


