Dementia is a major factor leading to dependency and disability of older people globally. It is a syndrome that leads to deterioration in thinking, remembering, ability to perform everyday activities and behaviour changes. It can cause cognitive disabilities and in most of the cases precedes changes in emotional control and social behaviors. Though dementia mostly affects people in the older age-groups, it should not be considered a regular problem of growing old. About 5-8% of the population above 60 years of age suffer from this disease. Dementia can affect the younger population as well in rare cases. People with dementia who are under 65 years of age account for 9% of total dementia cases. Dementia in this population is known as young onset dementia.
Identify dementia in early stages
In early stages people generally tend to overlook the symptoms of dementia which are – losing track of time, forgetfulness and getting lost even when the place is familiar. Generally, the onset of symptoms is more gradual in the early stages and starts getting more clearer as the disease progresses to the middle stage.
In the middle stage people start getting forgetful of things that have happened recently or names of the people whom they have met recently. They find difficulty in communicating and start needing help for personal care. Behaviour like wandering and repeated questioning starts getting evident.
In the late stage there is total dependence on others for day-to-day activities. There are serious memory disturbances and total unawareness of time and place. People find difficulty in recognizing friends and relatives. There can be aggressiveness in behavior and difficulty in walking.
Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia
Alzheimer’s is the most common form of dementia with 60–70% of total dementia cases. Other major forms of dementia are dementia with Lewy bodies (abnormal aggregates of protein inside the nerve cells), vascular dementia, and a group of diseases resulting in frontotemporal dementia (degeneration of brain’s frontal lobe). There are indistinct boundaries between different forms of dementia. Mixed forms of different types of dementia are quite common.
Preventive measures and treatment
As per the studies, risk of dementia can be reduced by following a healthy lifestyle like no smoking, no use of tobacco, no use of alcohol, regular exercise, good eating habits, keeping weight in control, maintaining blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar levels from younger age itself. We should always be occupied in cognitive activities and have good social interactions to prevent the chances of dementia at any point of life.
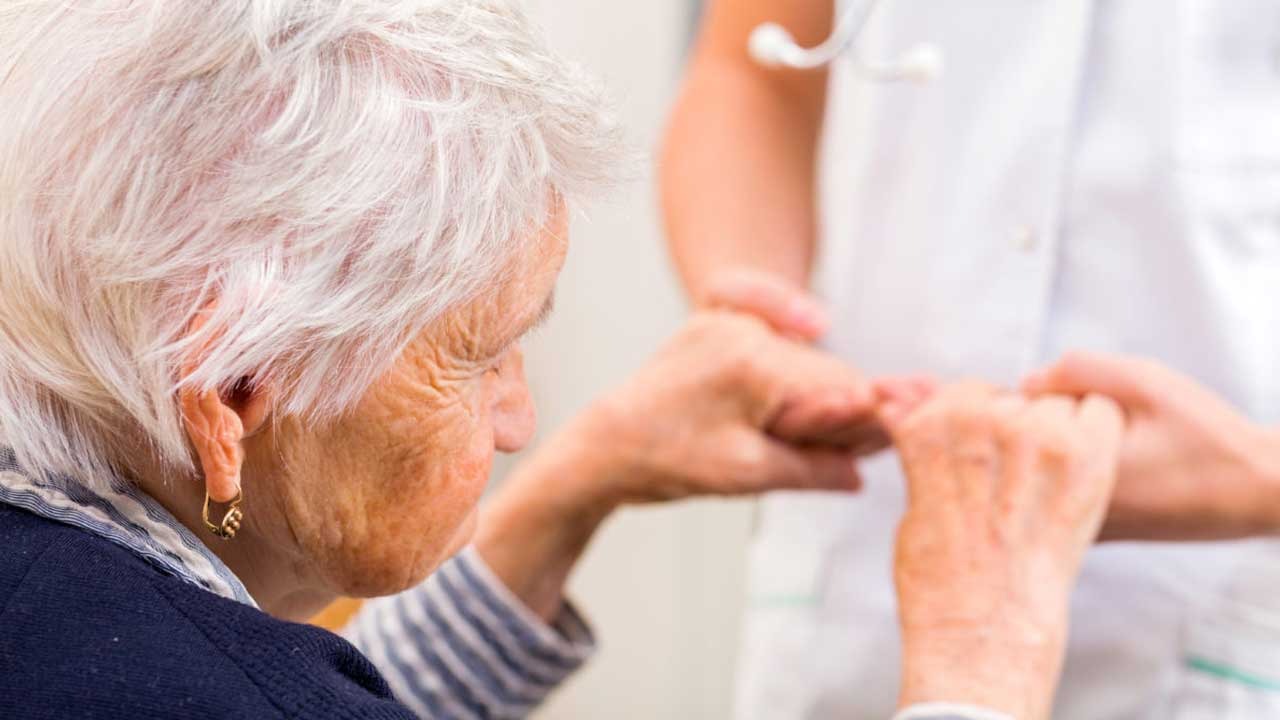

 According to WHO, there are 50 million people who are suffering from dementia worldwide, and there are nearly 10 million new cases of dementia every year. The most common form of dementia is Alzheimer's, which constitutes 60-70% of total dementia cases.
According to WHO, there are 50 million people who are suffering from dementia worldwide, and there are nearly 10 million new cases of dementia every year. The most common form of dementia is Alzheimer's, which constitutes 60-70% of total dementia cases.







.jpg)










.jpeg)



.jpg)







.jpeg)

.jpg)


