This exploration, distributed in Nature, shows how various populaces of individuals share the majority of the hereditary susceptibilities to creating type 2 diabetes yet have some unique hereditary varieties that can make them pretty much defenseless to building up the condition. This genome-wide meta-investigation of 433,540 East Asians, incorporating 77,418 with type 2 diabetes, is the consequence of two research consortia - AGEN (Asian Genetic Epidemiology Network) and DIAMANTE (DIabetes Meta-ANalysis of Trans-Ethnic affiliation considers).
At last, the objective of such investigations is to recognize potential hereditary focuses to treat or even fix the ceaseless metabolic issue that influences more than 400 million grown-ups around the world, as per the International Diabetes Federation.
Such an enormous scope study could never have been conceivable without the responsibility and devotion to the joint effort among such huge numbers of researchers around the globe, particularly in Asia," said Karen Mohlke of UNC-Chapel Hill. "The information this group gathered and examined has given the exploration network truly necessary new data about the natural underpinnings of diabetes."
In the new examination of East Asian people, specialists utilized genome-wide affiliation information from 23 companion concentrates in China, South Korea, Japan, Singapore, the Philippines, Hong Kong, Taiwan, and the United States to analyze type 2 diabetes hazard. For instance, they discovered a new relationship close to qualities GDAP1, PTF1A, SIX3, ALDH2, and qualities that influence muscle and fat separation. At another locus, specialists discovered two covering type 2 diabetes hereditary signs that seem to act through two qualities, NKX6-3 and ANK1, in various tissues.
"We realize diabetes is brought about by a mind-boggling set of hazard factors, for example, BMI, that effects affect the malady across family lines," said Xueling Sim, of the National University of Singapore. "These discoveries extend the number of hereditary variations related to diabetes and feature the significance of considering various family lines."
Co-first creator Cassandra Spracklen, Ph.D., associate teacher of biostatistics and the study of disease transmission at the University of Massachusetts at Amherst School of Public Health and Health Sciences, led a considerable lot of the investigations for the Nature paper while a postdoctoral individual in Mohlke's lab.
"Finding out about the extra variations can help recognize extra qualities that impact an individual's hazard for creating type 2 diabetes," Spracklen said. "These qualities show us more the pathophysiology of diabetes and could, at last, become helpful targets."
This exploration could help clarify why - among individuals of comparative weight file (BMI) or midriff perimeter - the predominance of type 2 diabetes is more prominent in East Asian populaces than in European populaces.
The following stages are to join disclosure across populaces and to tentatively figure out which qualities are changed by the hereditary variations and how those modifications lead to sickness.
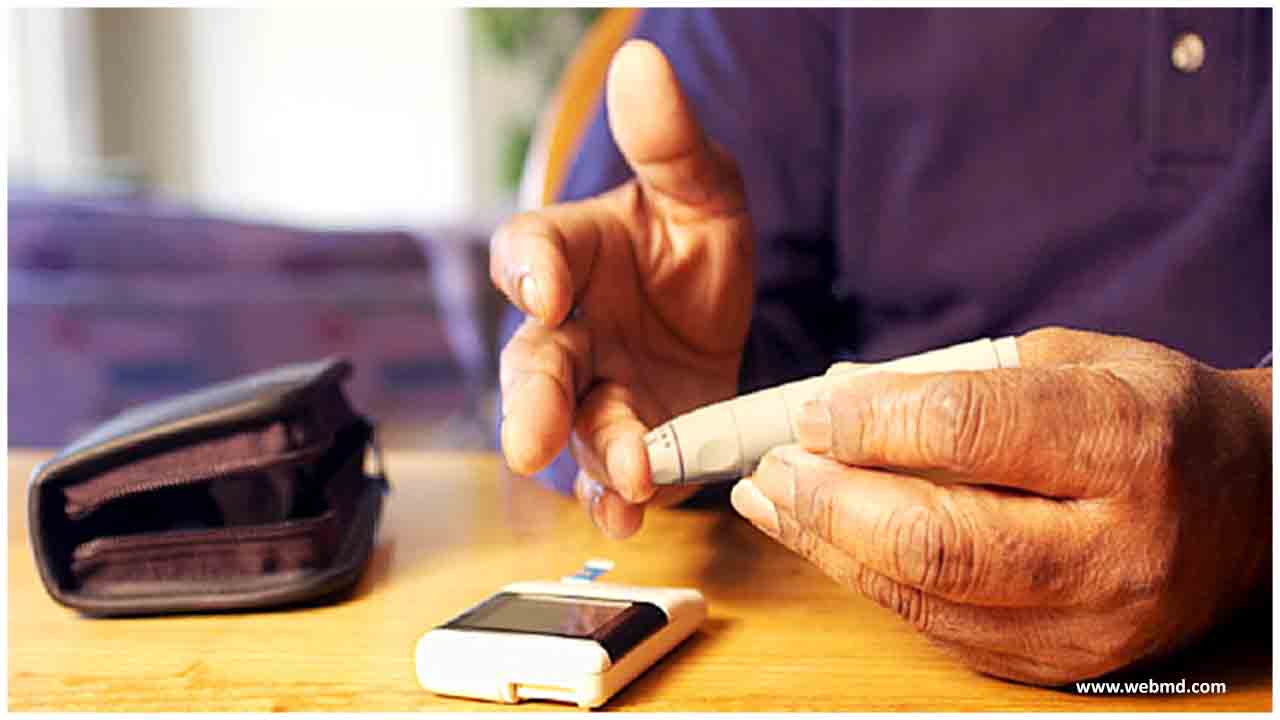
 In the largest study of its kind in any non-European population, an international team of researchers identified 301 distinct genetic signals at 183 loci, or specific positions on a chromosome, associated with type 2 diabetes in people from East Asia.
In the largest study of its kind in any non-European population, an international team of researchers identified 301 distinct genetic signals at 183 loci, or specific positions on a chromosome, associated with type 2 diabetes in people from East Asia.
















.jpeg)

.jpeg)










.jpg)




.jpg)

