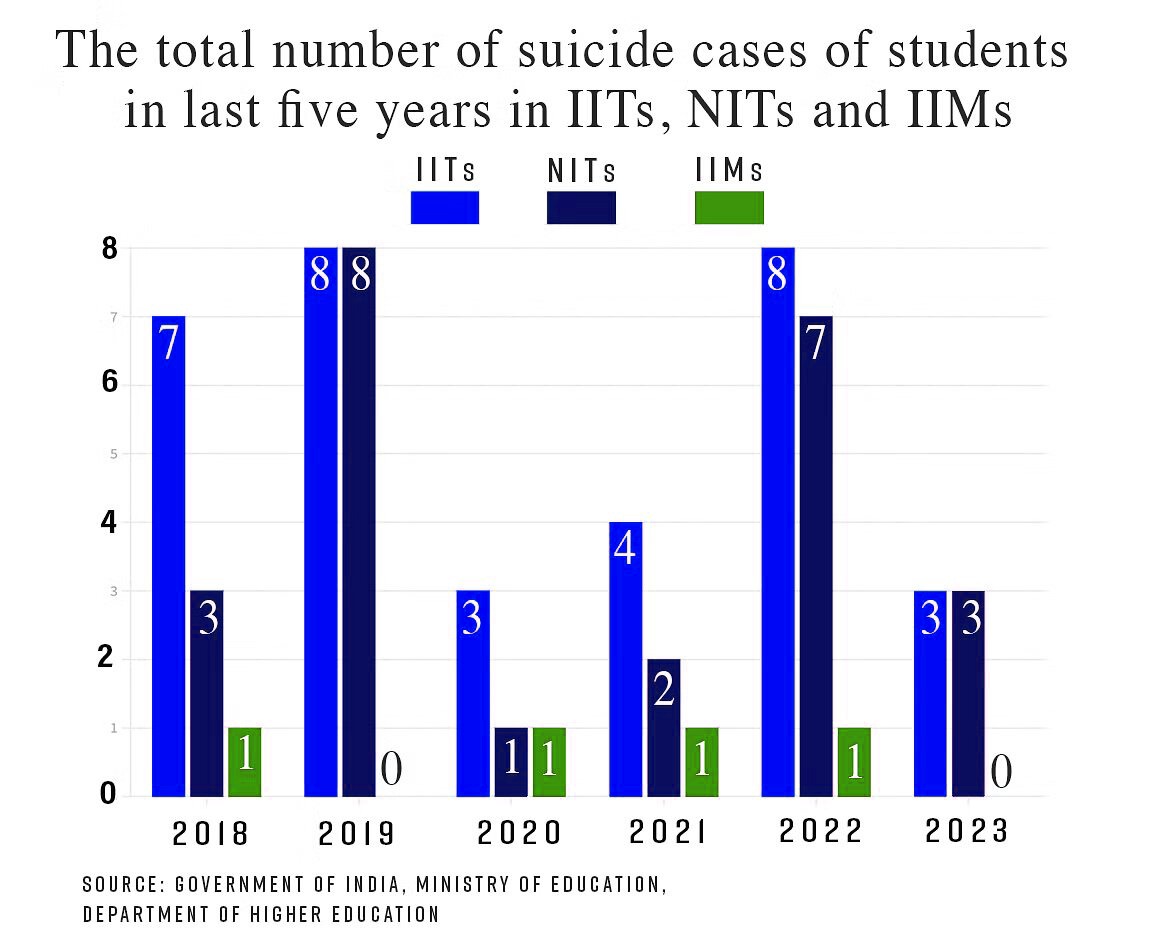
In a concerning revelation, the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) have reported the highest number of student suicide cases in the last five years, according to data shared by the education ministry with the Rajya Sabha. Between 2018 and 2023, a total of 98 student deaths by suicide were reported from top higher education institutions in India. Among these, 39 occurred at IITs, 25 each at National Institutes of Technology (NITs) and centrally-funded universities, and 13 at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) from 2019 onwards.
Possible Causes of Student Suicides in Premier Institutions:
Academic Pressure: The intense competition and high expectations for academic performance in premier institutions can lead to overwhelming stress and anxiety among students.
Isolation and Loneliness: Students may feel isolated and lonely, especially when away from their families and support networks, which can worsen feelings of despair.
Lack of Emotional Support: Limited interactions with faculty and peers due to various reasons may deprive students of crucial emotional support.
Family Expectations: The burden of fulfilling family expectations and the fear of disappointing loved ones can place immense pressure on students.
Financial Strain: Financial difficulties, especially for students from economically weaker backgrounds, can cause significant distress.
Mental Health Issues: Undiagnosed or untreated mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, or adjustment disorders can contribute to suicidal thoughts.
Social Discrimination: Students from reserved categories and minority communities may face discrimination and prejudice, adding to their emotional burden.
It is concerning to note that a majority of these suicides are reported among students from reserved categories, including SC/ST/OBC, and minority communities.
Precautions and Solutions to Address Student Suicides:
Recognizing the gravity of the situation, the government has taken some measures to address mental health concerns among students in higher education institutions. The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 has provisions for counseling to help students cope with stress and emotional challenges. Additionally, the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) has undertaken the translation of technical books into regional languages to ease language barriers and improve learning outcomes for students.
Furthermore, the recent release of the Redressal of Grievances of Students Regulations, 2023, by the University Grants Commission (UGC), mandates that all higher education institutions establish student grievance redressal committees (SGRC) that include members from marginalized castes or tribes and women to address student complaints effectively.
However, it is evident that more comprehensive efforts are needed to tackle the issue of student suicides in premier institutions. The institutions themselves must take a proactive approach to build a robust support system for their students. Which can include:
1. Mental Health Support Services: Establishing well-equipped counseling centers with trained professionals to provide confidential mental health support to students.
2. Awareness Campaigns: Conducting regular awareness campaigns to reduce the stigma surrounding mental health issues and promote the importance of seeking help.
3. Peer Support Programs: Creating peer support networks where students can connect, share experiences, and offer emotional support to one another.
4. Faculty Training: Training faculty and staff to recognize signs of distress and providing them with resources to offer appropriate support and referrals.
5. Early Intervention: Implementing early warning systems to identify at-risk students and intervene promptly to prevent crises.
6. Flexible Academic Environment: Allowing flexibility in academic schedules, course loads, and examination patterns to reduce academic pressure.
7. Inclusive Campus Culture: Promoting an inclusive campus environment that celebrates diversity and provides equal opportunities for all students.
8. Family Counseling: Involving families in the student support process, emphasizing the importance of empathy and understanding.
9. Mental Health Education: Incorporating mental health education into the curriculum to raise awareness and build emotional resilience.
10. Holistic Approach: Adopting a holistic approach to student well-being, addressing physical, emotional, and psychological needs.
11. Helpline Services: Providing 24/7 helpline services for students in crisis, offering immediate support and guidance.
12. Collaboration with NGOs: Collaborating with non-governmental organizations specializing in mental health to enhance support services.
The rising number of student suicides in premier institutions is a distressing issue that demands collective attention and action. While the NEP and recent regulations by the UGC are steps in the right direction, institutions must actively prioritize the mental health and emotional well-being of their students. By fostering a supportive and inclusive environment and providing necessary mental health resources, we can work towards reducing the prevalence of student suicides and ensuring a healthier academic journey for all students.
 Institutions must actively prioritize the mental health and emotional well-being of their students. By fostering a supportive and inclusive environment and providing necessary mental health resources, we can work towards reducing the prevalence of student suicides and ensuring a healthier academic journey for all students.
Institutions must actively prioritize the mental health and emotional well-being of their students. By fostering a supportive and inclusive environment and providing necessary mental health resources, we can work towards reducing the prevalence of student suicides and ensuring a healthier academic journey for all students.




















.jpeg)

.jpeg)










.jpg)




.jpg)

