An ongoing heatwave in Siberia that saw temperature records tumble as the locale boiled in 38-Celsius highs was "practically impossible" without the impact of artificial environmental change, driving researchers said Wednesday.
A global group of analysts found that the record-breaking warm period was more than 2C more smoking than it would have been if people had not warmed the planet through many years of ozone harming substance discharges.
The five most sweltering a very long time in history have happened over the most recent five years and there's a superior than-even possibility that 2020 will be the most sizzling at any point recorded.
Earth's posts are warming quicker than the remainder of the planet, and temperatures in Siberia - home to a great part of the world's carbon-rich permafrost - were more than 5C more sultry than normal among January and June.
One town, Verkhoyansk, recorded a temperature of 38C - crushing past records.
Andrew Ciavarella, the senior location and attribution researcher at Britain's Met Office, depicted the discoveries as "faltering".
"This is additional proof of the outrageous temperatures we can hope to see all the more as often as possible around the globe in a warming atmosphere," he said.
The effect of environmental change on extraordinary climate occasions, for example, super tempests and dry spells is currently entrenched, however until decently as of late researchers have been not able to authoritatively connect an individual occasion to an unnatural weather change.
As a component of a developing zone of atmosphere research known as attribution science, the group had PC recreations of fevers with the atmosphere as it is today - around 1C more sultry than the pre-Industrial time standard.
They at that point contrasted this with a model creating temperatures over Siberia this year without human impact - that is, without the extra synthetic 1C.
They found that the delayed warmth would happen not exactly once at regular intervals without human-initiated environmental change.
This makes the heatwave "practically unthinkable in an atmosphere that had not been warmed by ozone harming substance emanations", the group stated, including that carbon contamination had made the outrageous occasion, at any rate, multiple times bound to happen.
- 'Significant for everybody' -
The group behind the counts focused on that the Siberian heatwave was an issue for the whole globe.
Some 1.15 million hectares of woodland going up on fire discharged a great many huge amounts of CO2 into the environment. Simultaneously, the fierce blazes and continued heatwaves quickened the area's permafrost dissolve.
This caused an oil tank based on solidified soil to fall in May, prompting one of the area's most exceedingly terrible ever oil slicks.
"Such a drawn-out warmth wave is significant, for its effect on individuals, yet additionally from a logical perspective," said Olga Zolina, from Russia's P.P. Shirshov Institute of Oceanography.
"The ice is extremely, significant for the most part for framing of climate and course. So such high temperatures are extremely significant for the entire globe."
While the exploration was arranged quickly and has not yet been exposed to peer-survey, creators said it delivered "among the most grounded aftereffects of any attribution study led to date."
- 'No possibility' -
The 2015 Paris atmosphere bargain submits countries to topping temperature ascends to "well-beneath" 2C (3.6 degrees Fahrenheit) above pre-mechanical levels and to make progress toward a 1.5C breaking point assuming there is any chance of this happening.
With the only 1C of warming up until this point, Earth is now struck by record-breaking dry seasons, out of control fires and super tempests made progressively intense by rising ocean levels.
To keep in accordance with the 1.5C objective, the United Nations says worldwide outflows must fall by 7.6 percent consistently this decade.
Sonia Seneviratne, from ETH Zurich's Department of Environmental Systems Science, said the examination demonstrated the heatwave was a case of "outrageous occasions which would have practically no possibility of occurring" without synthetic outflows.
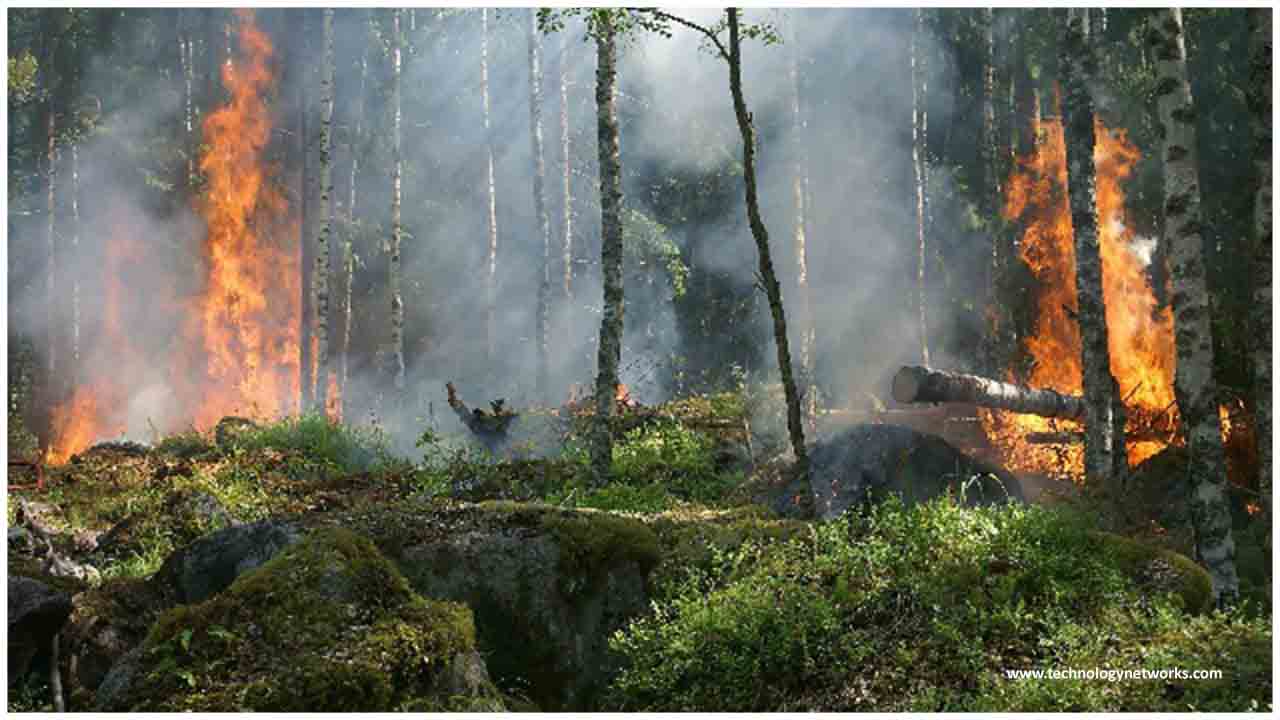

 Experts have found that extreme heat events such as the Siberian hot spell would happen less than once every 80,000 years without human-induced climate change.
Experts have found that extreme heat events such as the Siberian hot spell would happen less than once every 80,000 years without human-induced climate change.


















.jpeg)


















.jpg)
.jpeg)