Despite their reputation as a staple in comfort food, potatoes are often misunderstood in the realm of health and nutrition. Far from being a dietary villain, recent research reveals that these humble tubers offer significant cardiovascular benefits, especially for individuals with Type 2 diabetes. A recent study led by Neda Akhavan, Assistant Professor at UNLV’s School of Integrated Health Sciences, sheds new light on how potatoes can be a beneficial component of a diabetes-friendly diet.
The Potato’s Nutritional Power: Potatoes are more than just a filling side dish; they are a powerhouse of nutrients. Packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber, especially in the skin, they can contribute positively to health when prepared in a health-conscious manner. Despite their reputation for being a high-carbohydrate, high-calorie food, research shows that potatoes, when consumed properly, can actually support heart health and improve metabolic outcomes.
Study Overview and Methodology: Akhavan’s study, funded by the Alliance for Potato Research and Education, is one of the first to explore the cardiovascular benefits of potatoes specifically for people with Type 2 diabetes. The study involved 24 participants, all of whom were managing their diabetes with medication. For 12 weeks, participants were given baked potatoes with skins, measuring 100 grams and containing 20 grams of carbohydrates per serving, as a daily snack or side dish.
The control group consumed a similar amount of white rice, matched for calories and carbohydrates. This comparison aimed to assess whether potatoes could be a healthier alternative to high-glycemic foods like white rice. Participants were allowed to enhance their potatoes with herbs, spices, or a small amount of butter but were advised against frying.
Key Findings and Implications: The results of the study were promising. Participants who consumed baked potatoes experienced several health benefits. There was a modest decrease in fasting blood glucose levels, improvements in body composition, and a reduction in waist circumference and resting heart rate. These changes indicate that incorporating potatoes into the diet, in place of high-glycemic foods, could be beneficial for managing Type 2 diabetes.
Akhavan emphasizes that potatoes, when prepared healthfully and consumed in moderation, can be a valuable addition to the diets of individuals with diabetes. The study found no harmful effects on health outcomes, and the observed benefits support the idea that potatoes can be part of a balanced diet.
The Nutritional Benefits of Potatoes: Potatoes are an excellent source of dietary potassium, surpassing even bananas in this regard. Potassium is crucial for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels and preventing Type 2 diabetes. Additionally, potato skins are rich in resistance starch, a type of fiber known to improve glucose control, lipid profiles, and satiety. Resistance starch helps manage blood sugar levels and supports overall digestive health.
Incorporating potatoes into a diet can also help increase feelings of fullness, making them a satiating choice that can help with weight management. This is particularly relevant for individuals trying to control their blood sugar levels and manage their weight.
Preparation and Moderation: The key to enjoying potatoes healthfully lies in their preparation. While boiling is an option, baking or roasting potatoes retains more of their potassium and fiber. Akhavan recommends preparing a large batch of baked or roasted potatoes as a convenient and nutritious option for busy individuals.
Moderation is crucial, as with all foods. Potatoes should be part of a well-rounded diet, not the sole focus. By combining them with other nutrient-dense foods and maintaining balanced portion sizes, individuals can reap the health benefits without overloading on carbohydrates.
Akhavan plans to expand her research to include a larger and more diverse participant population. Future studies will explore the effects of incorporating potatoes into various dietary patterns, including the Mediterranean diet. This research aims to further understand the role of potatoes in dietary patterns and their broader health benefits.
Potatoes, often unfairly criticized in the nutrition world, are emerging as a valuable food for managing Type 2 diabetes and supporting heart health. With their rich nutrient profile and cardiovascular benefits, they offer a practical and healthful addition to the diets of those managing diabetes. By focusing on proper preparation and moderation, individuals can enjoy the benefits of potatoes while maintaining a balanced diet. As research continues, it is clear that this versatile tuber deserves a place in the conversation about healthy eating and diabetes management.
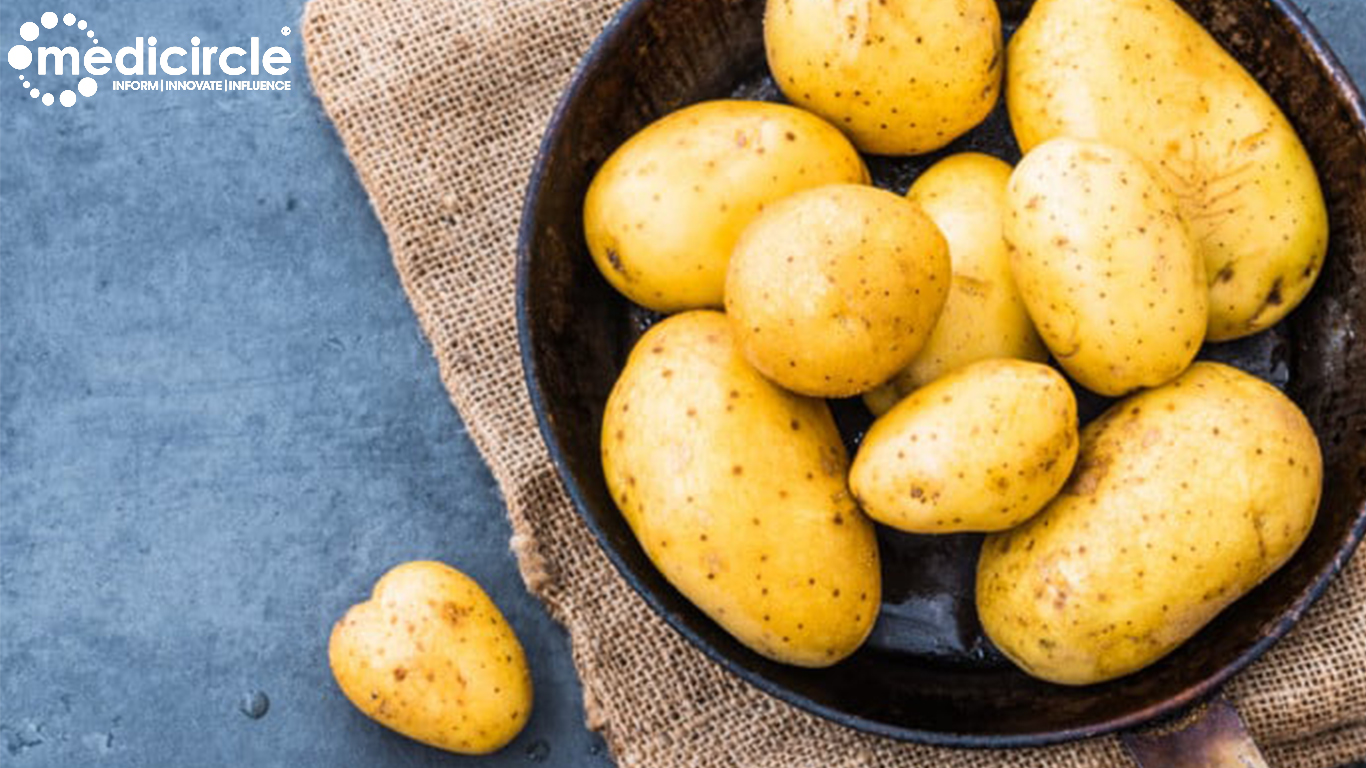

 Far from being a dietary villain, recent research reveals that potatoes offer significant cardiovascular benefits, especially for individuals with Type 2 diabetes.
Far from being a dietary villain, recent research reveals that potatoes offer significant cardiovascular benefits, especially for individuals with Type 2 diabetes.





.jpeg)


.jpg)
.jpg)









.jpeg)

.jpeg)










.jpg)




.jpg)

