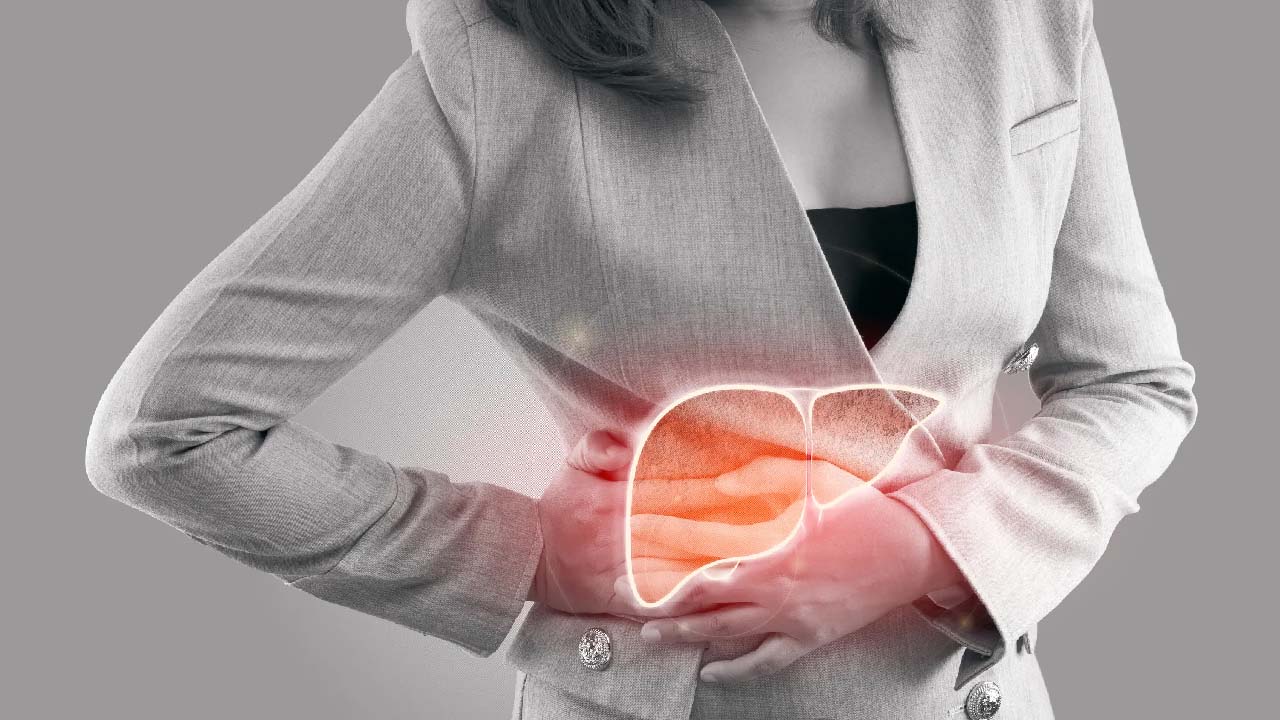
People who consume little to no alcohol are at risk for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), an umbrella term for various liver diseases. As the name suggests, NAFLD is characterized by excess fat in the liver cells.
There has been an increase in NAFLD prevalence worldwide, particularly in Western countries. In addition, about a quarter of Americans suffer from this chronic liver disease, making it the most widespread. People with NAFLD risk developing the more aggressive form of fatty liver disease known as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is characterized by liver inflammation and can eventually lead to scarring and liver failure (cirrhosis). Harm induced by excessive alcohol consumption is comparable to this type of damage.
Possible signs and symptoms you might be experiencing
If you've ever wondered what causes fatty liver disease, you've come to the right place. It is because it might occur with no apparent signs or symptoms. The liver fat of most NAFLD patients does not cause any damage to the organ. NASH develops in a small number of patients with liver fat.
NASH can cause symptoms such as Tiredness, Weakness, Weight-loss, Skin or eye yellowing, Spider-like blood vessels, and Chronic itch. In addition, fluid retention, internal bleeding, muscle wasting, and disorientation can all be indications of NASH progressing to cirrhosis. When cirrhosis progresses to liver failure, it may necessitate a liver transplant.
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Reality Check
NAFLD affects up to 25% of persons in the United States, which may appear unbelievable when viewed in raw figures. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the accumulation of fat in liver cells that is not caused by drinking. A small amount of fat is quite average in the liver. A fatty liver, on the other hand, is one in which fat comprises 5–10% of the liver's total weight (steatosis). So which people are more likely to suffer from NAFLD?
Diabetes, obesity, high cholesterol, and high triglycerides are risk factors for developing it. In addition to rapid weight loss and poor eating habits, NAFLD can also be caused by metabolic syndrome. However, NAFLD can occur in people who have no known risk factors. NAFLD has been related to several serious health issues. The liver may swell as a result of this (steatohepatitis). An enlarged liver can develop into scarring (cirrhosis) and potentially liver cancer or liver failure if left untreated for a long time.
Strangely, NAFLD can go unnoticed over long periods. Even if you don't have symptoms, they can include:
- Exhaustion
- Weakness
- Weight loss
- Nausea
- Abdominal pain
- Spider-like blood vessels
- Yellowing skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Itching
- Fluid build-up in the legs and abdomen and mental confusion.
NAFLD might be difficult to identify if there are no visible symptoms or if various diseases could cause the symptoms. The first sign of NAFLD is when blood tests show elevated liver enzyme levels. However, additional tests are carried out to rule out other liver illnesses. An ultrasound may be performed to confirm the diagnosis of NAFLD.
Keeping a healthy lifestyle is the most crucial factor.
People with fatty liver disease should educate themselves about the disease and engage closely with their healthcare providers. To avoid liver damage, you must disclose all of your drugs to your doctors. Supplements, vitamins, and over-the-counter medications are a few examples of this category. Can also manage fatty liver diseases by staying healthy, eating a well-balanced diet with enough fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, exercising regularly, and abstaining from alcohol.
Disclaimer: The content on this site is for informational purposes only, and should not be taken as professional medical advice. Always seek the guidance of your doctor or health professionals for any questions you may have regarding your health or a medical condition.

 An introduction to the world of Non-alcoholic Fatty liver disease. It is important to know the causes and symptoms moreover strict action needs to be taken as well. Let us take you through the guide so that you are well aware of the same.
An introduction to the world of Non-alcoholic Fatty liver disease. It is important to know the causes and symptoms moreover strict action needs to be taken as well. Let us take you through the guide so that you are well aware of the same. 










.jpeg)



.jpeg)

.jpg)





.png)




.jpg)
