A recent study by the World Health Organization (WHO) has revealed a disturbing trend: around a quarter of adolescent girls who have been in relationships have suffered physical or sexual violence. This analysis, published in the Lancet medical journal, highlights the urgent need for prevention and support measures for young women worldwide.
Key Findings of the Study: The WHO study analyzed data from surveys of thousands of girls aged 15 to 19 across 154 countries. The results are staggering:
- 24% of adolescent girls have experienced intimate partner violence at least once.
- 16% reported experiencing violence in the past year alone.
Dr. Lynnmarie Sardinha, the lead author of the study, expressed concern that younger women are often overlooked and do not receive the necessary support. She was surprised by the high percentage of adolescent girls subjected to violence before reaching adulthood. The data collection spanned from 2000 to 2018, with more recent data still under verification, indicating only a slight decline in these numbers.
The acts of violence reported in the survey included physical violence, such as kicking or hitting, and unwanted sexual acts, including rape or attempted rape. The study's data, broken down by country and region, shows a strong correlation between violence and women's rights.
- Oceania and Africa reported the highest rates of intimate partner violence, with Papua New Guinea at 49% and the Democratic Republic of Congo at 42%.
- Europe reported the lowest rates, with 10% of girls experiencing such violence.
This regional disparity highlights the significant impact of socio-economic factors and women's rights on the prevalence of intimate partner violence. Countries where women and girls have limited access to education and face unequal inheritance laws showed higher levels of violence.
Dr. Pascale Allotey, Director of WHO’s Sexual and Reproductive Health and Research department, emphasized the severe and long-lasting harm caused by violence during these critical formative years. She stressed that intimate partner violence among adolescents must be recognized as a major public health issue, warranting focused prevention efforts and targeted support.
The profound effects of violence on young women include not only immediate physical injuries but also long-term psychological trauma. It can disrupt their education, limit their economic opportunities, and increase the likelihood of experiencing violence later in life. Addressing this issue is crucial for breaking the cycle of violence and ensuring healthier futures for young women.
The WHO study highlights the need for comprehensive strategies to prevent intimate partner violence and support victims. These strategies should include:
- Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the signs of intimate partner violence and educating young people about healthy relationships can help prevent abuse.
- Legal and Policy Reforms: Strengthening laws and policies to protect women and girls from violence and ensure their rights are upheld.
- Access to Services: Providing accessible support services, including counseling, medical care, and legal assistance, for victims of violence.
- Community Engagement: Involving communities in efforts to change social norms that condone violence against women and girls.
The WHO study's findings on intimate partner violence among adolescent girls are a wake-up call for governments, organizations, and communities worldwide. With one in four young girls experiencing violence in their relationships, there is an urgent need for coordinated efforts to protect and empower these vulnerable individuals. By implementing comprehensive prevention and support measures, we can work towards a future where all young women can live free from violence and achieve their full potential. By addressing this pressing issue with targeted actions, we can help create a safer and more equitable world for all young women.
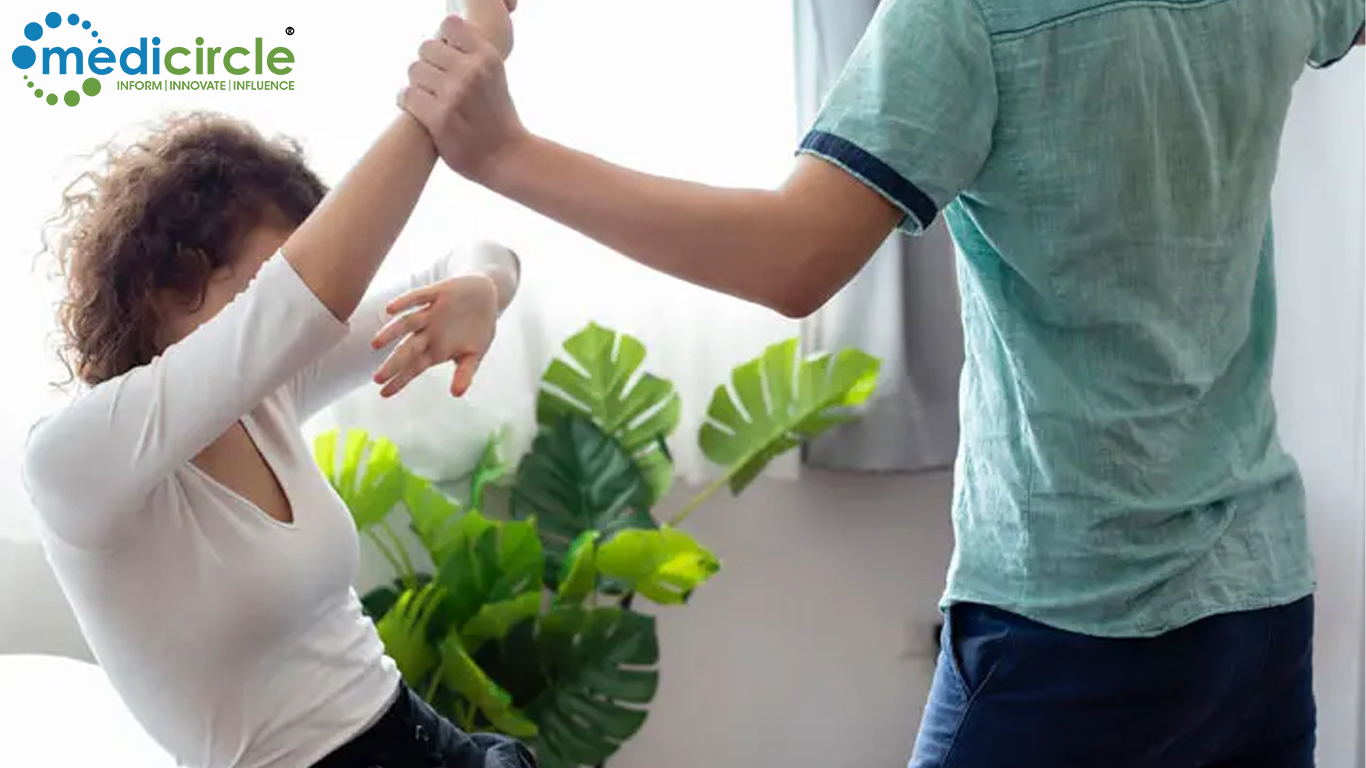

 Dr. Lynnmarie Sardinha, the lead author of the study, expressed concern that younger women are often overlooked and do not receive the necessary support. She was surprised by the high percentage of adolescent girls subjected to violence before reaching adulthood.
Dr. Lynnmarie Sardinha, the lead author of the study, expressed concern that younger women are often overlooked and do not receive the necessary support. She was surprised by the high percentage of adolescent girls subjected to violence before reaching adulthood.










.jpeg)






.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)