Merck, known as MSD outside the United States and Canada, today announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved an expanded label for KEYTRUDA, Merck’s anti-PD-1 therapy, as monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL). The approval is based on results from the Phase 3 KEYNOTE-204 trial in which KEYTRUDA significantly reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 35% (HR=0.65 [95% CI, 0.48-0.88; p<0.0027]) compared to brentuximab vedotin (BV). Additionally, median progression-free survival (PFS) was 13.2 months (95% CI, 10.9-19.4) for patients treated with KEYTRUDA and 8.3 months (95% CI, 5.7-8.8) for patients treated with BV. The FDA also approved an updated pediatric indication for KEYTRUDA for the treatment of pediatric patients with refractory cHL, or cHL that has relapsed after two or more lines of therapy.
“An estimated 8,500 patients in the U.S., many of them 40 years of age or younger, will be diagnosed with cHL this year. Now patients with cHL who progress after frontline therapy have a new option in KEYTRUDA, which has demonstrated a clinically meaningful improvement in progression-free survival compared to brentuximab vedotin,” said Dr Vicki Goodman, vice president, clinical research, Merck Research Laboratories. “At Merck, we are committed to improving outcomes for patients with cancer. Today’s FDA approval builds upon our growing range of options for people with blood cancers.”
Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur with KEYTRUDA, including pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, severe skin reactions, solid organ transplant rejection, and complications of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, KEYTRUDA should be withheld or discontinued and corticosteroids administered if appropriate. KEYTRUDA can also cause severe or life-threatening infusion-related reactions. Based on its mechanism of action, KEYTRUDA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. For more information, see “Selected Important Safety Information” below.
“The patients with cHL who do not achieve remission following initial treatment or who relapse after transplantation face a poor prognosis, reflecting the unmet need for improved therapies in the relapsed/refractory setting,” said Dr John Kuruvilla, hematologist and associate professor of medicine, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre and University of Toronto. “With this approval, KEYTRUDA has the potential to change the current standard of care and help these patients achieve better outcomes.”
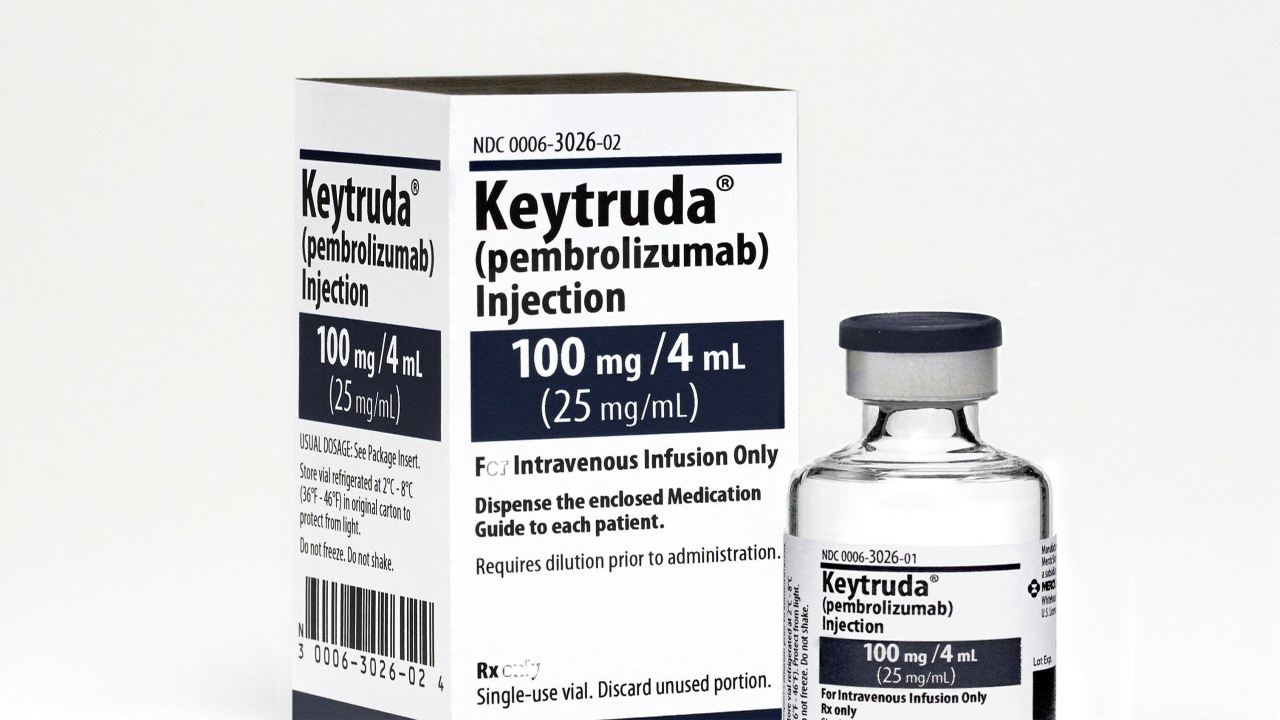
 FDA approves expanded indication for Merck’s KEYTRUDA (pembrolizumab) in adult patients with relapsed or refractory classical hodgkin lymphoma (cHL)
FDA approves expanded indication for Merck’s KEYTRUDA (pembrolizumab) in adult patients with relapsed or refractory classical hodgkin lymphoma (cHL)



















.jpeg)

.jpeg)
.jpeg)

.jpeg)


.jpeg)



.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)


.jpg)


.jpeg)
.jpeg)