Ultrasound is widely used for conducting physical examinations, and plans are underway for expanding its application to the treatment of Parkinson's disease, dementia, and diabetes. A research team at National Tsing Hua University led by Associate Professor Yu-Chun Lin of the Institute of Molecular Medicine and Professor Chih-kuang Yeh of the Department of Biomedical Engineering and Environmental Sciences has successfully improved the motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease in mice by injecting cellular proteins that are highly sensitive to ultrasound waves into the deep brain region and afterwards using ultrasound to activate the neuron cells.
Their innovative research has been published in the January issue of Nano Letters, and their non-invasive treatment has already been patented in Taiwan and the US.
Lin has long sought to find a safe, non-invasive way to control cell activity. Although light waves are safe, they can only penetrate to a depth of about 0.2 cm; magnetic waves can penetrate deep, but lack precision. By contrast, ultrasonic waves penetrate to a depth of up to 15 cm, and can be focused on the affected part. Thus, the challenge was how to make cells respond to ultrasound.
Lin said that almost all mammals have a kind of high-frequency auditory pressure protein known as prestin. However, the prestin in the human body has little sensitivity to ultrasound. By contrast, the prestin in dolphins, whales, and sonar bats is highly sensitive to ultra-high frequency sound waves. By comparing their prestin protein sequences, Lin found that they all have a special amino acid, which he colonized into the cells of mice to modify their prestin proteins. This resulted in an immediate tenfold increase in the cells’ ability to sense ultrasound.
Lin’s next task was to find a way to use ultrasound to treat diseases, for which purpose he turned to ultrasound expert Yeh, who devised a way to enclose prestin gene fragments in tiny bubbles which can be imported into the target area by intravenous injection. As soon as the ultrasound is applied, the bubbles break, introducing the gene fragments into the target cells, thereby activating their ability to detect and respond to ultrasound.
“Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease are caused by the degeneration and death of the cells in the brain. But once the cells with prestin gene fragments have been transplanted into the target area, ultrasound can be applied to awaken atrophied cells so that they can begin to form new neural connections,” Yeh said.
The team has produced a video showing how a mouse with Parkinson's disease stops short while crossing a wooden bridge, and how the same mouse, following cell transplantation and ultrasound treatment, crosses the bridge easily. It has also been found that the treatment results in a significant increase in dopamine levels in the brain, demonstrating its effectiveness in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Lin said that this same procedure can also be used to treat diabetes by stimulating insulin-producing cells.
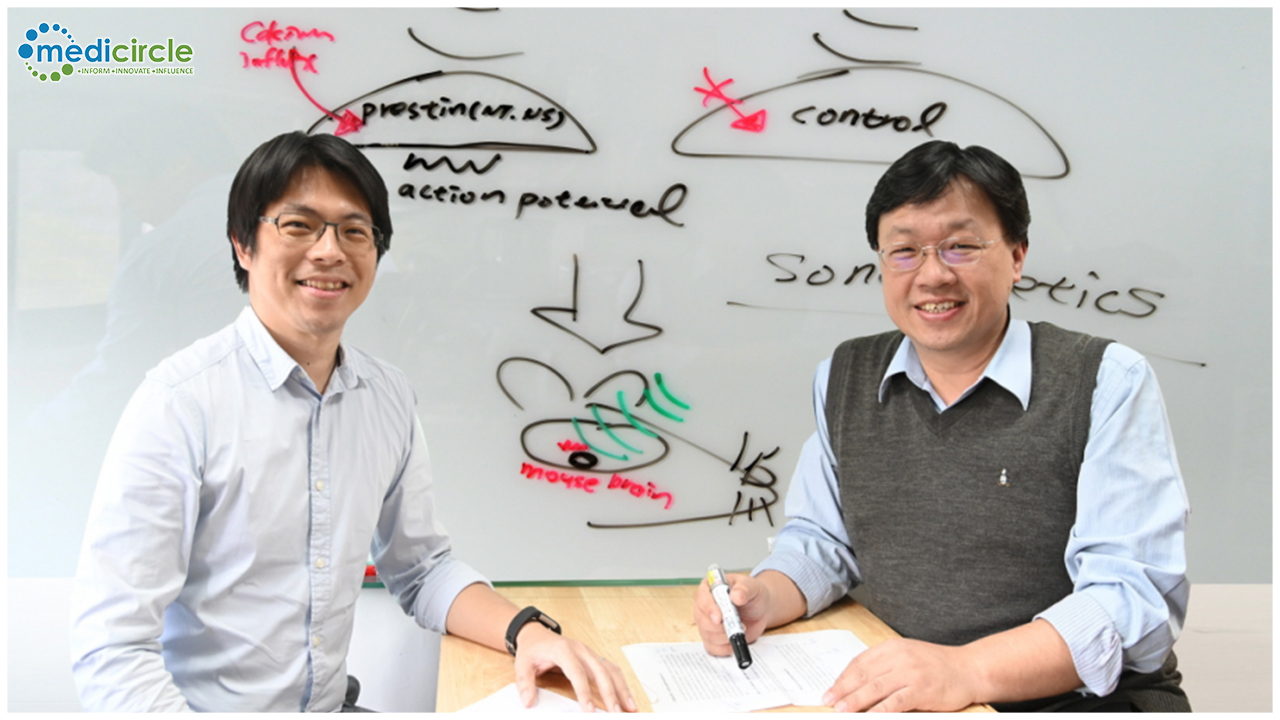
 “Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease are caused by the degeneration and death of the cells in the brain. But once the cells with prestin gene fragments have been transplanted into the target area, ultrasound can be applied to awaken atrophied cells.
“Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease are caused by the degeneration and death of the cells in the brain. But once the cells with prestin gene fragments have been transplanted into the target area, ultrasound can be applied to awaken atrophied cells.



















.jpeg)








.jpg)




.jpg)




