Swine flu is commonly known as H1N1 flu and is majorly caused by the H1N1 strain. It is a subtype of the Influenza A virus. Its symptoms are the same as that of seasonal flu. The H1N1 virus has evolved from pigs, birds and humans that cause diseases in humans. In 2009, WHO declared H1N1 flu as an epidemic that got over in 2010. The available flu vaccine is not effective against H1N1 flu.
Swine flu - Signs and symptoms
Fever, Headache, Chills, Cough, Sore throat, Runny nose, Diarrhoea. Fatigue. The symptoms appear after 1-2 days of exposure to the virus.
Seasonal flu – It is caused due to influenza virus type A and B. Symptoms are the same as that of swine flu-like fever, cough, sore throat, runny nose. Influenza vaccines are available and are being updated from time to time. WHO recommends annual vaccination for high-risk groups. Children and adults should ideally get vaccinated just before the flu season begins.
Swine flu causes - Viruses such as H1N1 infect the cells that line your nose, throat, and lungs. The virus enters your body when you inhale contaminated droplets or transfer the live virus from a contaminated surface to your eyes, nose, or mouth.
Complications associated with H1N1 virus - Neurological signs and symptoms, ranging from confusion to seizures Respiratory failure Worsening of chronic conditions, such as heart disease and asthma PneumoniaPrevention
The Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) endorses annual flu vaccination for everyone above 6 months. The flu vaccine reduces the risk of getting flu and its severity and lowers the risk of getting hospitalized. The flu vaccine is available as an injection and as a nasal spray. The nasal spray is approved for use in healthy people ages 2 through 49 years old. Nasal sprays are not recommended for pregnant women.
Measures to be taken
Wash your hands regularly and thoroughly – Use soap and water and if it is not available, use hand sanitizer. Cover your face while coughing or sneezing – You can use your elbows and then wash your hands. Clean surfaces on regular basis – Regularly clean often touched surfaces to prevent the spread of infection. Avoid touching your face – Avoid touching your eyes, nose, and mouth. Maintain social distance – Avoid gatherings if it is possible. Avoid anyone who is sick. If you are at high risk – pregnant, or with co-morbidities or senior citizen - consider avoiding swine barns at seasonal fairs and elsewhere.COVID 19 and Influenza virus
COVID-19 and influenza viruses have a similar disease presentation. They both affect the respiratory system of the human body causing cough, sore throat, and congestion. Both viruses are transmitted by contact, droplets, and fomites. Thus, following hand hygiene is of utmost importance to keep viruses away.
The speed of transmission is an important point of difference between the two viruses. Influenza has a shorter median incubation period (the time from infection to appearance of symptoms) and a shorter serial interval (the time between successive cases) than the COVID-19 virus. The serial interval for the COVID-19 virus is estimated to be 5-6 days, while for the influenza virus, the serial interval is 3 days. This means that influenza can spread faster than COVID-19.
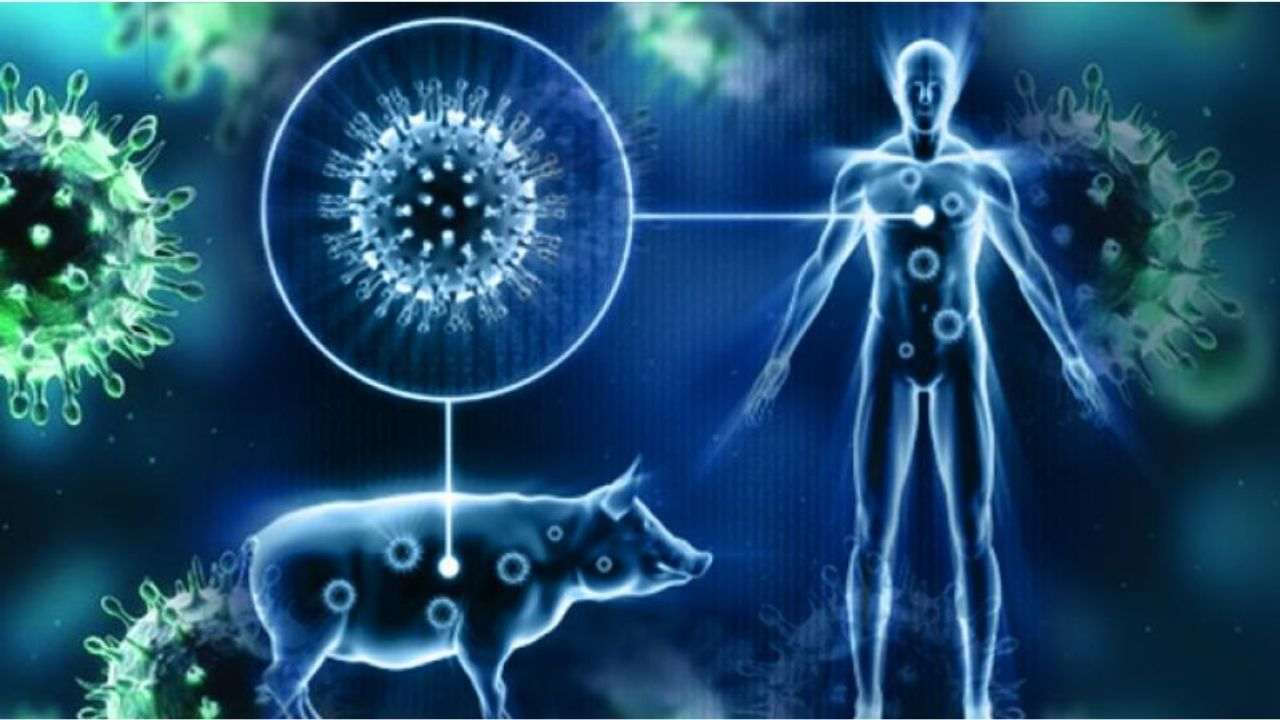
 Know the difference between Swine flu and COVID infection and protect yourself against them by taking appropriate measures
Know the difference between Swine flu and COVID infection and protect yourself against them by taking appropriate measures










.jpeg)






.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)