Anxiety is a normal and natural emotional response to stress and danger. While experiencing anxiety occasionally has become a common feature of modern life, excessive anxiety can be problematic and may interfere with daily functioning. Anxiety can vary in intensity from person to person.
According to the GOQii India Fit Report 22-23 stress and mental health study conducted among 10,000+ Indians, indicates that 24 per cent of Indians are struggling with stress and mental health issues.
Some common forms of anxiety are as follows
1. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): GAD is often disproportionate to the actual threat, it involves excessive worry and tension about various aspects of life such as work, health, relationship, or everyday situations.
2. Panic Disorder: Panic attacks can be a sudden attack triggered in response to specific situations, during which an individual may experience a combination of physical symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, sweating, a rapid heartbeat, or loss of control.
3. Social Anxiety Disorder: Also known as Social Phobia, Social Anxiety is a mental health condition in which social interactions cause anxiety.People with social anxiety experience extreme self-consciousness, fear of judgment or embarrassment and avoid social interactions.
4. Specific Phobias: Specific Phobias are fears of specific objects, situations, and activities. Some common examples include fear of heights, spiders, flying, or public speaking.
Causes of Anxiety
1. Genetics: Research suggests that having a family history of anxiety or mental health conditions can increase the chances of an individual experiencing anxiety.
2. Brain Chemistry: Imbalances in brain chemicals such as serotonin, dopamine, or norepinephrine can contribute to anxiety symptoms.
3. Traumatic Experiences: Witnessing traumatic events such as accidents, abuse, or violence can impact mental health and cause anxiety.
4. Environmental Factors: Chronic stress, major life changes, and work or academic pressures can increase vulnerability to anxiety.
5. Personality Traits: Certain personality traits such as being highly sensitive, perfectionistic, or having a tendency towards negative thinking may increase the likelihood of experiencing anxiety.
Symptoms of Anxiety
1. Physical Symptoms may include increased heart rate, shortness of breath, gastrointestinal issues, trembling, and sweating.
2. Psychological Symptoms can manifest as persistent worry, fear, irritability, disturbances in sleep, and facing difficulty concentrating.
Understanding the above-listed symptoms can help individuals and their near and dear ones identify anxiety-related challenges.
Managing And Treating Anxiety
1. Self-Care: Prioritize self-care by engaging in activities that promote relaxation and reduce stress. Regular exercise, sufficient sleep, a healthy diet, and mindfulness practices like meditation or deep breathing exercises can contribute to overall health.
2. Seeking Support: Don't hesitate to reach out to friends, family, or support groups who can provide a listening ear and understanding. Professional help from therapists, psychologists, or psychiatrists can be invaluable in developing coping mechanisms and exploring treatment options.
3. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a widely-used therapeutic approach for anxiety. It helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and replace them with more constructive and realistic thinking.
4. Stress Management Techniques: Learning stress management techniques such as time management, setting boundaries, and practising relaxation techniques like yoga can reduce anxiety.
5. Medication: In some cases, healthcare professionals may prescribe medication to manage severe anxiety symptoms. It is important to consult a medical professional to determine if medication is the right option and to ensure proper dosage and monitoring.
(It is important to note that anxiety disorders are treatable conditions. Seeking professional help from mental health professionals, such as therapists or psychiatrists, can provide individuals with effective strategies for managing and reducing anxiety symptoms. Additionally, self-care practices, stress management techniques, and support from loved ones can contribute to overall well-being and anxiety reduction.
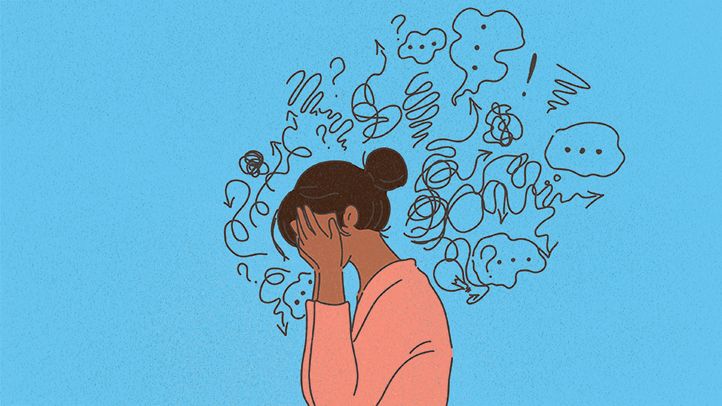

 Anxiety has become a pervasive issue in today's fast-paced world, affecting millions of individuals worldwide.Let's explore the causes, symptoms, and impact of anxiety, shedding light on the invisible battle that many face in their day-to-day life
Anxiety has become a pervasive issue in today's fast-paced world, affecting millions of individuals worldwide.Let's explore the causes, symptoms, and impact of anxiety, shedding light on the invisible battle that many face in their day-to-day life


















.jpeg)











.jpg)




.jpg)


